HVAC CFM Calculator
Calculate the required CFM for your HVAC system
HVAC CFM Calculator
Room 1
Total Required CFM
Based on your room configurations and occupants
CFM Breakdown
Enter room details to see CFM breakdown
What is HVAC CFM Calculation?
HVAC CFM calculation determines the cubic feet per minute (CFM) of airflow needed to properly ventilate or condition a space. It’s a key part of HVAC system design that ensures adequate air circulation, indoor air quality, and overall comfort.
To calculate CFM, you’ll need a few essential inputs: room dimensions (length, width, height), the desired number of air changes per hour (ACH), and the total room volume.
Once calculated, the CFM value helps HVAC professionals select the right air conditioning units, exhaust fans, or ventilation systems to meet the space’s ventilation requirements.
A proper CFM ensures:
- Good airflow and air quality
- Improved cooling or heating performance
- Reduced health risks from stale or poorly circulated air
CFM requirements can vary depending on the room type: bedrooms, kitchens, offices, or basements all need different airflow levels to maintain optimal conditions.
How to Use Our Free CFM Calculator?
Figuring out the right airflow (CFM) for a room is about numbers + making your space feel comfortable, fresh, and healthy.
Here’s how our calculator simplifies that:
Step 1: Enter your room dimensions
What to do: Add your room’s length, room width, and ceiling height in feet.
Why it matters: This gives us the room’s total air volume in cubic feet, which is the foundation of your CFM calculation. A bigger volume means more air to circulate, and therefore, higher airflow demand.
Example: A room measuring 20 ft × 15 ft × 8 ft = 2,400 cubic feet of air to move.
Step 2: Choose room-specific settings
What to do: Select details like room type (e.g., kitchen, bedroom), window type, number of windows, sun exposure, and insulation quality.
Why it matters: These factors help estimate how heat, sunlight, and insulation impact your space’s ventilation needs.
For example, a kitchen with average insulation and sun exposure may need more airflow than a shaded, well-insulated bedroom.
Triple-pane windows + high sun exposure + poor insulation = increased required airflow.
Step 3: Add the number of occupants
What to do: Enter how many people typically occupy the room.
Why it matters: Every person breathes, generates heat, and affects indoor air quality. We account for this by adding CFM per person, usually 5–15, depending on use case.
7 people × 5 CFM per person = 35 additional CFM added to your total airflow requirement.
Step 4: Instantly get your total required CFM
Our calculator runs the numbers and shows the exact amount of airflow (in cubic feet per minute) your space needs, factoring in:
- Room size
- ACH (Air Changes Per Hour)
- Environmental factors
- Occupancy load
✅ Example result: “You need 510 CFM for this room setup.”
This helps you size your HVAC unit, plan ductwork, or configure an exhaust fan or air purifier with confidence.
Understanding HVAC CFM
Getting the airflow right in any space starts with understanding CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute). CFM measures how much air your HVAC system, air purifier, or ventilation system moves every minute. Whether you’re improving air circulation in a bedroom or calculating airflow for a commercial space, knowing your CFM is key to ensuring comfort, health, and energy efficiency.
Why is proper CFM essential for your space?
The precise calculations ensure that the ventilation required in your space is circulated and refreshed at the rate it needs to be. Without it, you might experience:
- Poor air quality: stagnant air, high humidity, and buildup of dust or CO₂
- Uneven cooling/heating: some areas feel hot while others stay cold
- System strain: Undersized airflow causes HVAC units to overwork, reducing their lifespan
- Health risks: inadequate ventilation leads to respiratory discomfort and indoor pollutants
For both homeowners and HVAC professionals, calculating CFM accurately helps optimize your system for comfort, air quality, and long-term performance.
The role of Air Changes Per Hour (ACH)
ACH stands for Air Changes Per Hour: how many times the total volume of air in a room is replaced every hour.
It’s a key factor in CFM calculation, as it directly impacts how quickly stale air is removed and fresh air is circulated. The higher the ACH, the more often the air in the room is replaced, which is essential for spaces like bathrooms, kitchens, or workshops where air contaminants or moisture build up quickly.
Recommended ACH rates for different spaces
Here’s a quick guide to standard ACH values used by HVAC professionals and air conditioning engineers.
These may vary depending on local codes or usage, but serve as solid starting points:
| Room Type | Recommended ACH |
| Bedrooms | 5 – 6 ACH |
| Living Rooms | 6 – 8 ACH |
| Kitchens | 7 – 9 ACH |
| Bathrooms | 8 – 10 ACH |
| Offices | 5 – 8 ACH |
| Laundry Rooms | 8 – 9 ACH |
| Basements | 3 – 4 ACH |
| Gyms/Home Studios | 8 – 10 ACH |
| Commercial Spaces | 6 – 12 ACH |
ACH values may vary depending on local climate and ventilation system performance.
How to Calculate CFM?
To determine the required CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) for proper airflow, use this simple formula:
CFM = (Room Volume × Air Changes per Hour) ÷ 60
Step-by-step calculation:
1. Measure your room volume: Multiply the length × width × ceiling height (all in feet) to get the cubic feet of the space.
2. Choose the recommended Air Changes per Hour (ACH): This depends on your room type and ventilation needs.
3. Apply the formula: Multiply the room volume by the ACH, then divide by 60 to convert hourly air changes to per-minute airflow.
Example calculation:
For a 12 ft × 10 ft room with an 8 ft ceiling and a desired 6 ACH:
Room volume = 12 × 10 × 8 = 960 cubic feet
CFM = (960 × 6) ÷ 60 = 96 CFM
Your HVAC or ventilation system should provide at least 96 CFM to maintain proper airflow.
Understanding your CFM calculation is just the start; what truly matters is how that number impacts your real-world space.
How to Convert CFM to Tons (AC Sizing Reference)
Once you know your total CFM requirement, the next question most people ask is: What size air conditioning system do I actually need? That’s where the CFM-to-tons conversion comes in.
The Standard Conversion
The industry standard rule of thumb:
1 ton of AC capacity = 400 CFM of airflow
So the formula is simple:
Tons = Total CFM ÷ 400
If your home needs 1,600 CFM of total airflow across all rooms, you’d need a 4-ton AC system to deliver it.
CFM-to-Tons Quick Reference Table

Home size ranges are approximate and assume standard 8 ft ceilings, average insulation, and moderate climate. Actual sizing depends on insulation quality, window area, sun exposure, local climate, and occupancy.
Climate Adjustments
The 400 CFM/ton rule is a baseline. Your local climate affects the ideal ratio:
- Humid climates (Southeast US, Gulf Coast): Use 350 CFM per ton. Lower airflow slows the air over the evaporator coil, improving moisture removal and dehumidification.
- Standard/moderate climates: Use 400 CFM per ton. The default ratio for most residential HVAC systems.
- Dry/arid climates (Southwest US, Mountain West): Use 450 CFM per ton. Higher airflow moves more air without the dehumidification concern, improving cooling efficiency.
If you need a more detailed load calculation that accounts for all these variables, insulation R-values, window U-factors, duct leakage, and heat gain, use our HVAC load calculator to get a precise tonnage recommendation.
CFM to Tons Converter
Convert your airflow requirement into AC system size
CFM to Tons Converter
Convert your airflow requirement into AC system size
CFM Requirements by Room Size: Quick Lookup Table
Don’t want to do the math? Use this table to look up the recommended CFM based on your room’s square footage and type.
All values assume standard 8 ft ceilings and mid-range ACH for each room type.
Residential CFM Chart
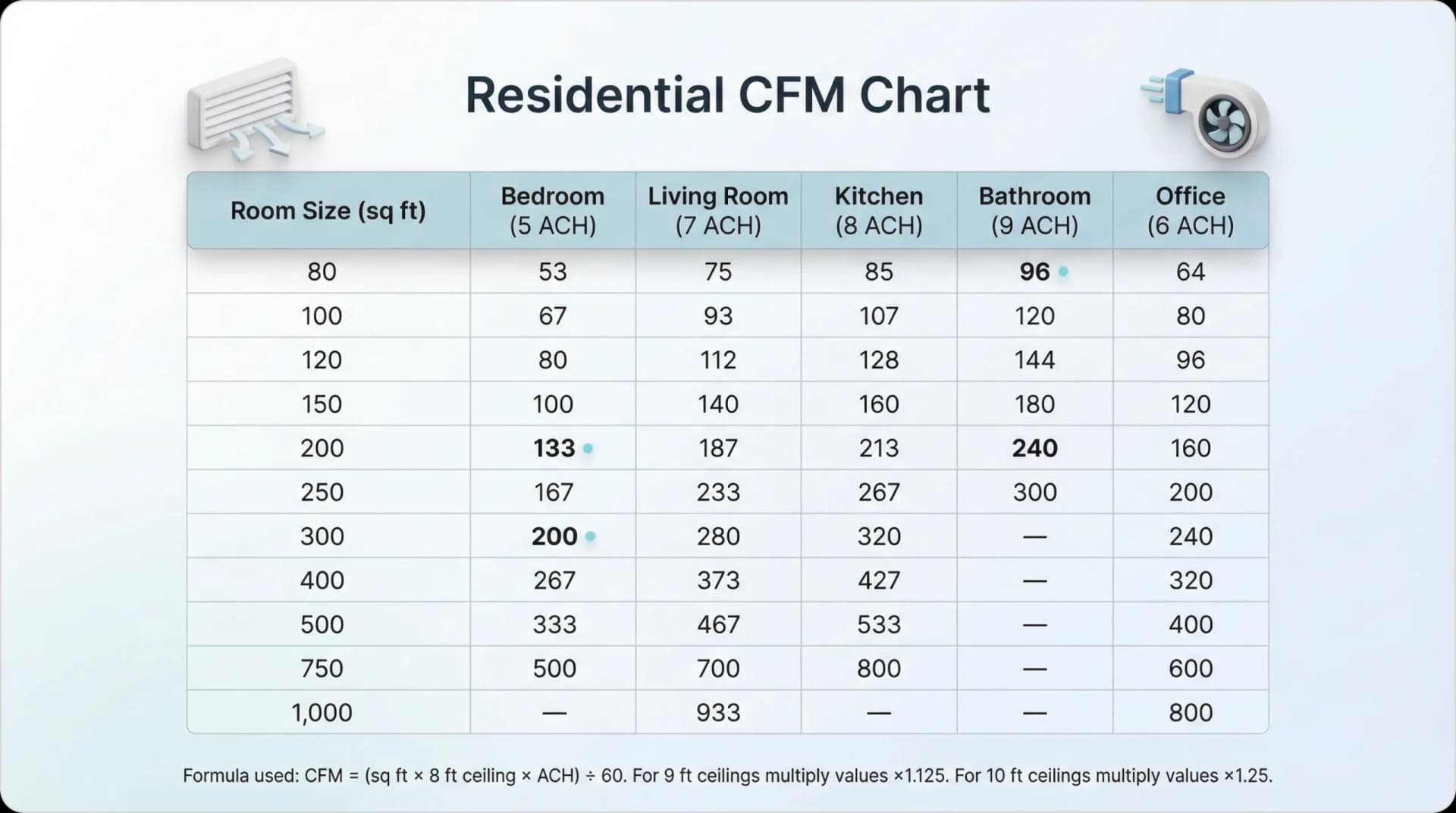
How to Read This Table
Find your room type across the top, then find your approximate square footage down the left side. The number in the cell is the CFM your HVAC system or ventilation fan should deliver to that room.
Example: A 200 sq ft kitchen needs approximately 213 CFM. A 300 sq ft living room needs about 280 CFM.
If you’re designing a full system and need to size ductwork to deliver these CFM values to each room, use our free duct sizing calculator to get the right duct dimensions for each run.
How Room Factors Affect Airflow Requirements?
The CFM numbers above are starting points. In practice, your actual airflow requirement shifts based on the specific conditions in the room. Here’s how each factor in the calculator adjusts the result and why it matters.
Insulation Quality
Insulation directly affects how hard your HVAC system works to maintain the temperature. Poor insulation means more heat transfer through walls and ceilings, which means the system needs to move more air to compensate.
| Insulation Level | Effect on CFM |
| Poor (older homes, no wall insulation) | +15–20% above baseline |
| Average (standard fiberglass batts, R-13 walls) | Baseline CFM |
| Good (upgraded insulation, R-19+ walls) | −5–10% below baseline |
| Excellent (spray foam, R-30+ attic, tight envelope) | −10–15% below baseline |
Window Type and Count
Windows are a major source of heat gain (summer) and heat loss (winter). More windows and lower-efficiency glass mean higher CFM requirements.
| Window Type | Effect on CFM |
| Single pane | +10–15% – significant heat transfer |
| Double pane | Baseline – standard for most homes built after 1990 |
| Triple pane | −5–10% – excellent thermal performance |
| No windows | −10–15% – no solar heat gain (basements, interior rooms) |
Each additional window adds incremental CFM demand, especially on south- and west-facing walls where sun exposure is highest.
Sun Exposure
Direct sunlight heats a room faster than any other factor. A south-facing room with floor-to-ceiling windows in Phoenix needs significantly more airflow than a north-facing room in Seattle.
| Sun Exposure Level | Effect on CFM |
| Heavy shade (trees, overhangs, north-facing) | −10% below baseline |
| Light shade (partial cover, east-facing) | −5% below baseline |
| No shade (unobstructed, south/west-facing) | Baseline |
| Good amount of sun (large windows, direct exposure) | +10–15% above baseline |
Occupancy
People generate heat (about 75 watts per person at rest) and CO₂. The more people in a room, the more airflow you need to maintain comfort and air quality.
The standard addition is 5 CFM per person, but ASHRAE recommends higher rates for densely occupied spaces like conference rooms, classrooms, and restaurants.
These adjustments compound. A poorly insulated kitchen with single-pane windows, heavy sun exposure, and 6 occupants will need substantially more CFM than the lookup table suggests. That’s why the calculator factors in all of these variables simultaneously.
Practical Applications & Considerations
Common Issues That Correct CFM Solves
Getting the CFM right addresses problems that homeowners and HVAC technicians deal with every day:
- Poor air circulation: rooms that feel stuffy even with the system running
- High indoor humidity: air isn’t moving fast enough to dehumidify properly
- Lingering odors: cooking smells, pet odors, and chemical fumes that won’t clear
- Dust buildup and stale air: a sign that air changes per hour are too low
- Health discomfort: headaches, fatigue, and respiratory irritation from poor ventilation
CFM in HVAC System Sizing
CFM is the bridge between knowing what a space needs and selecting the right equipment to deliver it. When a system is sized without accurate CFM calculations, the consequences show up fast:
- Short cycling: the system turns on and off too frequently because the airflow doesn’t match the load
- Frozen coils or overheating: airflow that’s too low or too high for the equipment’s design
- Rooms that never reach target temperature: the system is running, but the air isn’t getting where it needs to go
- Energy waste and higher utility bills: the system compensates by running harder and longer
If you’re an HVAC contractor building proposals around these numbers, our free HVAC estimate template gives you a professional format to present system recommendations and pricing to clients.
And once the install is done, the HVAC invoice template keeps your billing clean and itemized.
When to consult a professional
While this calculator gives a reliable airflow estimate for individual rooms, there are situations where it’s best to bring in an HVAC professional or air conditioning engineer, such as:
- Large commercial or multi-room buildings
- Spaces with unusual ceiling height or complex layouts
- Duct design or static pressure issues
- Indoor spaces with high occupant loads (like gyms, conference rooms, or workshops)
- When ventilation requirements vary across zones
For HVAC contractors who want a deeper resource on pricing these jobs, this detailed HVAC pricing guide covers hourly rates, flat-rate models, and how to build profitable proposals around load calculations like this one.
For HVAC Professionals: Turn Calculations Into Business
If you’re a technician or contractor using this CFM calculator during client walkthroughs, site assessments, or system design, the number you get here is the starting point for a job proposal.
Here’s how CFM calculations connect to the rest of your workflow:
- Estimating – Use your CFM calculation to size the system, then build a professional quote with FieldCamp’s HVAC estimate template. Include equipment specs, labor, and materials in one clean document.
- Pricing – Make sure your rates cover your true costs. FieldCamp’s labor cost calculator helps you factor in wages, insurance, taxes, and overhead. The service price calculator builds in your target margin. And the profit margin calculator verifies your numbers before you send the proposal.
- Invoicing – After the install, generate a detailed invoice with the HVAC invoice template that itemizes equipment, ductwork, labor, and startup/commissioning.
- Getting paid – For maintenance contracts (quarterly filter changes, annual tune-ups, seasonal inspections), set up recurring invoices and automatic payment collection so you’re not chasing checks every cycle. Here’s how: Auto-Deducting Payments for Invoices & Recurring Jobs.
If you’re managing jobs, crews, and invoicing across multiple clients, FieldCamp’s HVAC field service software puts scheduling, dispatching, and billing in one platform.
Here’s a walkthrough on managing invoices: Creating and Managing Invoices in FieldCamp.
Still Doing HVAC Calculations on Paper? There’s a Faster Way to Run Your Business.
You can calculate CFM all day, but if your scheduling is in a spreadsheet, your estimates are in Word docs, and your invoices are in QuickBooks, you’re spending more time on admin than on actual HVAC work.
Other HVAC businesses in your market are already running this way. The longer you wait, the more jobs and time you’re losing to competitors who figured it out first.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to calculate ACH in HVAC?
ACH (Air Changes Per Hour) tells you how many times the total volume of air in a room gets replaced in one hour. To calculate it from existing airflow: ACH = (CFM × 60) ÷ Room Volume. If a room is 960 cubic feet and your system delivers 96 CFM to that room, then ACH = (96 × 60) ÷ 960 = 6 air changes per hour. That means the entire volume of air in that room is fully replaced six times every hour.
How much CFM do I need per square foot?
The general rule is about 1 CFM per square foot for residential spaces with standard 8 ft ceilings and average conditions. But this varies significantly by room type. Kitchens and bathrooms need more airflow (1.3–1.5 CFM per sq ft) because of moisture, heat, and odors. Bedrooms need less (0.7–0.8 CFM per sq ft). The actual number depends on ceiling height, insulation, window area, sun exposure, and how many people use the space. Use the CFM lookup table above to get a more accurate number for your specific room.
How do you test HVAC CFM?
1 CFM equals one cubic foot of air moving past a point every minute. To put that in perspective, one cubic foot is roughly the size of a basketball. So 100 CFM means 100 basketball-sized volumes of air being moved every single minute. It’s the standard unit used across the HVAC industry to measure how much air a system, fan, or vent can supply or exhaust.
How do you calculate CFM for HVAC?
Use the formula: CFM = (Room Volume × ACH) ÷ 60. First, calculate room volume by multiplying length × width × ceiling height (all in feet). Then choose the recommended ACH for that room type: bedrooms at 5–6, kitchens at 7–9, bathrooms at 8–10. Plug those numbers in and divide by 60 to convert from hourly air changes to per-minute airflow. Add 5 CFM per occupant on top of the result. The calculator at the top of this page does all of this automatically.
How do I convert CFM to tons of AC?
Divide your total CFM by 400. That’s the standard conversion: 400 CFM = 1 ton of cooling capacity. So if your whole home needs 1,200 CFM of total airflow, you’d need a 3-ton AC system. In humid climates, use 350 CFM per ton for better dehumidification. In dry climates, use 450 CFM per ton for more efficient cooling. See the full CFM-to-tons conversion table above for a quick reference.
What CFM do I need for a 1,000 square foot house?
For a typical 1,000 sq ft home with 8 ft ceilings, you’ll need approximately 800–1,000 total CFM depending on room layout and usage. A rough estimate: living areas at ~7 ACH, bedrooms at ~5 ACH, kitchen at ~8 ACH, and bathrooms at ~9 ACH. Add it all up, and you’re looking at roughly 800–1,000 CFM total, which translates to a 2–2.5 ton AC system. Use the room-by-room calculator above for a precise breakdown based on your actual floor plan.
What is the difference between CFM and ACH?
CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) measures the volume of air moving through a system or into a room every minute. ACH (Air Changes per Hour) measures how many times the total air in a room gets fully replaced in one hour. They’re related by the formula: CFM = (Room Volume × ACH) ÷ 60. Think of ACH as the goal (how fresh you want the air) and CFM as the delivery requirement (how much airflow your system needs to hit that goal). You set ACH based on room type, and CFM is what your equipment needs to deliver.
How does duct size affect CFM?
Undersized ducts restrict airflow and reduce the CFM reaching each room. even if your HVAC system has enough capacity. Oversized ducts slow air velocity, which can cause poor air distribution and temperature inconsistency. The right duct size depends on the CFM that the room requires and the target air velocity (typically 600–900 feet per minute for residential trunk lines). Once you know your per-room CFM from this calculator, use our duct sizing calculator to determine the correct duct dimensions for each run.