HVAC Load Calculator
Calculate the required cooling capacity for your room
Total wattage of computers, servers, or other heat-generating equipment
Cooling Requirement
Note:
This is an estimate. For precise calculations, consult with an HVAC professional. Factors like ductwork condition, number of floors, and local building codes can affect the actual load.
How to Use This HVAC Calculator?
You don’t need HVAC experience to use this tool. Here’s how it works:
Step 1 – Enter your room size: Type in the room length, width, and ceiling height. If you’re calculating for a whole house, run the calculator once per room and add up the totals.
Step 2 – Tell us about your home: Select your climate zone, insulation quality, sun exposure, window type, number of exterior doors, room type, and whether you have major appliances in the space. If you’ve got computers, servers, or other equipment generating heat, enter the wattage in the device heat field.
Step 3 – Get your results: Hit “Calculate HVAC Load.” You’ll see your total BTU requirement, a recommended system size in tons, and a line-by-line breakdown of how each factor contributed to your result.
You can download the report as a file or email it directly to a client or contractor.
That’s it. The whole thing takes under two minutes.
Need to figure out airflow after sizing your system? Use our free HVAC CFM calculator to calculate the cubic feet per minute your ducts need to deliver.
How This HVAC Load Calculator Works?
Most online HVAC calculators use a flat “20 BTU per square foot” rule and call it a day. That’s fine for a rough guess, but it ignores half the variables that actually affect your cooling load.
Our calculator uses an adjusted square footage method that factors in seven variables most tools skip. Here’s the actual formula running behind the scenes:
Total BTU/h =
(Room Area × Climate Factor × Ceiling Adjustment × Insulation Multiplier × Sun Exposure Factor)
+ (Occupants × 600)
+ (Windows × Window Type BTU)
+ (Exterior Doors × 1,000)
+ Room Type Adjustment
+ Appliance Heat Load
+ Device Heat (Watts × 3.412)
Climate Zone Factors
| Zone | BTU per sq ft | Regions |
| Hot | 27 | Southern states (TX, FL, AZ) |
| Moderate | 20 | Central states (TN, NC, MO) |
| Cold | 15 | Northern states (MN, NY, WI) |
Insulation Multipliers
| Quality | Multiplier | Description |
| Poor | 1.3× | Older home, drafty, minimal insulation |
| Average | 1.1× | Standard insulation, some air leaks |
| Good | 1.0× | Newer home, well-insulated |
| Excellent | 0.85× | Energy-efficient build, tight construction |
Sun Exposure Factors
| Exposure | Multiplier | Description |
| Strong | 1.1× | South or west-facing walls, minimal shade |
| Average | 1.0× | Partial shade, mixed exposure |
| Shaded | 0.9× | North-facing, heavy tree cover, interior room |
Window Heat Gain (per window)
| Window Type | BTU |
| Single-pane | 1,200 |
| Double-pane | 1,000 |
| Low-E or triple-pane | 700 |
Room Type Adjustments
| Room Type | Adjustment | Reason |
| Kitchen | +2,000 BTU | Cooking generates significant heat |
| Office | +500 BTU | Equipment and electronics |
| Living Room | +0 BTU | Baseline |
| Bedroom | −400 BTU | Lower activity, fewer heat sources |
| Other | +0 BTU | — |
Appliance Load
- Kitchen with major appliances checked: +4,000 BTU
- Any other room with appliances checked: +2,000 BTU
Device Heat
Converted from watts to BTU at the standard rate of 3.412 BTU per watt. So 500 watts of computer equipment adds about 1,706 BTU to your cooling load.
We publish these numbers because you should be able to verify the math yourself. Most HVAC calculators treat their formulas like a black box. We’d rather show you exactly how your result was calculated.
HVAC Load Calculation Example
Let’s walk through a real scenario so you can see how the numbers come together.
Suppose you have a living room with these specs:
- 20 ft long × 15 ft wide (300 sq ft)
- 10 ft ceilings
- Hot climate (Houston, TX)
- Average insulation
- Average sun exposure
- 3 occupants
- 4 double-pane windows
- 1 exterior door
- No major appliances
- 200 watts of electronics (TV, lamp, router)
Here’s how the calculator breaks it down:
| Component | Calculation | BTU |
| Base envelope load | 300 sq ft × 27 × 1.25 × 1.1 × 1.0 | 11,138 |
| Occupant heat gain | 3 people × 600 BTU | 1,800 |
| Window heat gain | 4 windows × 1,000 BTU | 4,000 |
| Door heat gain | 1 door × 1,000 BTU | 1,000 |
| Room type adjustment | Living room | 0 |
| Appliance heat gain | None | 0 |
| Device heat gain | 200 watts × 3.412 | 682 |
| Total | 18,620 BTU/h |
Tonnage: 18,620 ÷ 12,000 = 1.55 tons → Recommended size: 1.5 Ton
That 1.5-ton unit is the right match. A 2-ton system would be oversized for this room, leading to short-cycling and poor humidity control, especially in a humid climate like Houston.
Once you know your system size, you can get a full cost breakdown: equipment, labor, and installation, in our detailed HVAC pricing guide.
HVAC Sizing Chart by Square Footage
This table gives you a quick reference for residential HVAC sizing in moderate climates. Use the calculator above for a more precise result based on your specific conditions.
| Home Size (sq ft) | BTU Estimate | System Size | Estimated Installed Cost |
| 600–900 | 18,000 | 1.5 Ton | $3,000–$4,500 |
| 1,000–1,200 | 24,000 | 2 Ton | $3,500–$5,500 |
| 1,300–1,600 | 30,000 | 2.5 Ton | $4,000–$6,500 |
| 1,700–2,000 | 36,000 | 3 Ton | $4,500–$7,500 |
| 2,100–2,400 | 42,000 | 3.5 Ton | $5,000–$8,000 |
| 2,500–2,800 | 48,000 | 4 Ton | $5,500–$9,000 |
| 2,900–3,300 | 60,000 | 5 Ton | $6,500–$11,000 |
Note: Cost ranges are based on 2025–2026 national averages for central AC systems, including equipment and standard installation. Your actual cost will depend on your region, the brand you choose, and the complexity of the install.
For a line-by-line breakdown of what goes into HVAC pricing, equipment costs, labor rates, permit fees, and markup, read our full HVAC pricing guide.
What Type of HVAC System Fits Your Load?
Knowing your BTU number is only half the answer. The other half is picking the right type of system. Here’s a general guide based on your calculated cooling load:
| BTU Range | Recommended System Type | Best For |
| Under 18,000 | Ductless mini-split | Single rooms, home additions, spaces without existing ductwork |
| 18,000–36,000 | Mini-split or small central | Small homes, apartments, condos |
| 36,000–60,000 | Central AC or heat pump | Standard single-family homes |
| 60,000+ | Multi-zone central system | Large homes, multi-story buildings |
A few things to keep in mind:
If you live in a moderate climate (zones 3–5), a heat pump can handle both heating and cooling, which means one system instead of two. In hot-humid climates, make sure whatever system you pick has good dehumidification, oversized units, short-cycle, and leave your home muggy.
If your home doesn’t have existing ductwork, a ductless mini-split is almost always cheaper to install than adding ducts for a central system. And if you’re replacing an existing central unit, make sure your ductwork can handle the new system’s airflow requirements.
Need to size your ductwork? Our HVAC duct size calculator can help you figure out the right duct dimensions based on your CFM and air velocity.
What Affects Your HVAC Load the Most?
Not every factor in the calculator carries the same weight. Square footage and ceiling height have the biggest impact on your cooling load, followed by climate zone and insulation quality. Sun exposure and windows matter, but less so. Appliances only move the needle in kitchens or rooms with heavy electronics.
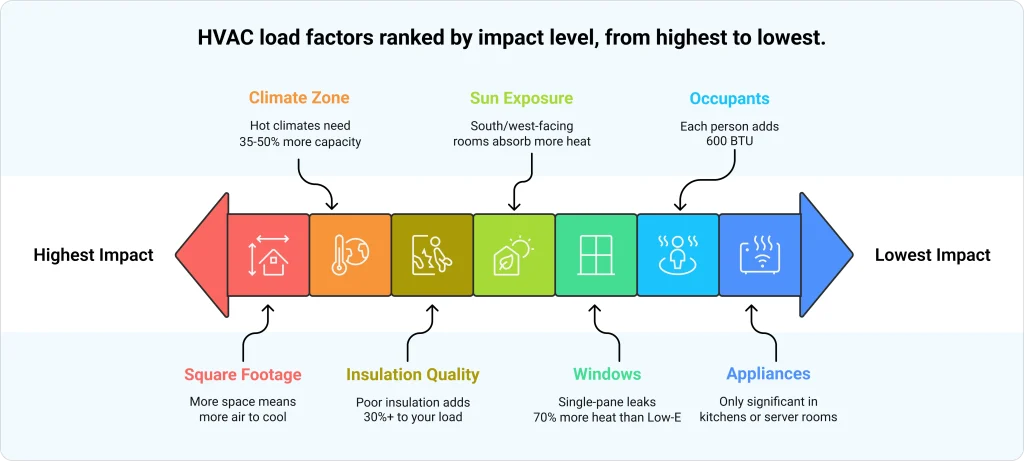
If you want to reduce your HVAC load without buying a bigger system, insulation upgrades and window replacements give you the most bang for your money. Sealing air leaks around doors, windows, and attic access points is often the cheapest fix with the biggest payoff.
Manual J vs. HVAC Load Calculator – Which Do You Need?
Manual J is the industry-standard method for residential HVAC sizing, developed by the Air Conditioning Contractors of America (ACCA). It’s thorough; a full Manual J assessment accounts for wall construction, R-values, infiltration rates, duct leakage, building orientation, shading, and dozens of other variables.
Our HVAC calculator is a simplified alternative. It uses an adjusted square footage method with real multipliers for climate, insulation, sun exposure, and window type. It’s not Manual J, but it’s significantly more accurate than the flat “20 BTU per square foot” rule most online calculators rely on.
When to Use Which
| Use Case | Manual J | This Calculator |
| Quick field estimate | No | ✓ |
| Validating a contractor’s quote | No | ✓ |
| Homeowner replacing an old unit | No | ✓ |
| Emailing a rough sizing to a client | No | ✓ |
| New construction permit | ✓ | No |
| Major remodel (adding rooms, etc.) | ✓ | No |
| Code-compliant system design | ✓ | No |
| Room-by-room airflow balancing | ✓ | No |
| Cost | $100–$300 | Free |
| Time | Hours | Under 2 minutes |
Bottom line: If you need a quick, reasonable estimate for a standard home, this calculator will get you there. If you’re pulling permits, doing new construction, or designing a system from scratch, hire a professional for a full Manual J assessment. Don’t guess on those.
Getting ready to send a quote after sizing a system? Grab our free HVAC estimate template, it’s pre-formatted so you can plug in the numbers and send a professional proposal in minutes.
Disclaimer
This HVAC calculator provides estimates for residential cooling load sizing based on simplified industry methods. Results are intended for general planning purposes; they are not a substitute for a professional Manual J assessment. For code-compliant system designs, new construction, or major remodels, consult a licensed HVAC professional. Actual cooling loads may vary based on duct condition, building materials, air infiltration, and other factors not captured by this tool.
You Just Saved 10 Minutes on Load Calcs.
Now imagine saving 10 hours a week on scheduling, invoices, and dispatch. That’s FieldCamp.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you calculate HVAC load?
Start with the square footage of the room or home. Multiply that by a climate-based BTU factor (15–27 BTU per sq ft, depending on your region), then adjust for ceiling height, insulation quality, sun exposure, and window type. Add heat from occupants (600 BTU per person), exterior doors (1,000 BTU each), appliances, and electronics. The total gives you the cooling load in BTU per hour. Divide by 12,000 to convert to tons. Our HVAC calculator does all of this automatically, you just enter the inputs, and it handles the math.
What is the rule of thumb for HVAC load calculation?
The most common rule of thumb is 20 BTU per square foot in moderate climates. So a 1,500 sq ft home would need roughly 30,000 BTU, or a 2.5-ton system. But this rule doesn’t account for insulation, ceiling height, window quality, or climate, which can swing your actual load by 30% or more in either direction. Use it as a sanity check, not a final answer.
What size HVAC system do I need for a 2,000 sq ft house?
In a moderate climate with average insulation and standard 8-ft ceilings, a 2,000 sq ft home typically needs 36,000–42,000 BTU, which translates to a 3 to 3.5-ton system. But that number shifts significantly based on your specific conditions. A 2,000 sq ft home in Phoenix with poor insulation and lots of south-facing windows might need a 4-ton unit. The same house in Portland with good insulation might only need 2.5 tons. Run the calculator with your actual specs for a more reliable number.
How much does a professional load calculation cost?
A full Manual J assessment from a licensed HVAC professional typically costs $100–$300, depending on the size of your home and your market. It’s worth the money for new construction, major remodels, or any situation where you need code-compliant documentation. For everyday system replacements and quick estimates, our free HVAC calculator gives you a solid starting point at no cost.
How accurate is an online HVAC calculator compared to Manual J?
An online calculator using the adjusted square footage method, like ours, is generally within 10–15% of a Manual J result for standard residential homes. That’s accurate enough for quote validation, early planning, and system comparisons. Where online calculators fall short is with unusual construction (log homes, ICF walls, passive house builds), multi-zone systems, or homes with significant duct losses. For those situations, Manual J is the right tool.
What happens if my HVAC system is too big?
An oversized HVAC system short-cycles; it cools the air quickly, shuts off, then kicks back on when the temperature rises. This creates four problems: (1) poor humidity control, because the system doesn’t run long enough to dehumidify, (2) uneven temperatures with hot and cold spots, (3) higher energy bills from constant start-stop cycling, and (4) faster wear on the compressor. Oversizing is one of the most common and expensive mistakes in residential HVAC. A properly sized system runs longer, more even cycles, which is actually what you want.
Can I use this calculator for commercial buildings?
This calculator is designed for residential spaces. For commercial buildings over 5,000 sq ft, the load calculation gets more complex; you need to account for occupancy patterns, ventilation requirements, internal heat from lighting and equipment at scale, and commercial duct design. We recommend working with a licensed mechanical engineer or using ACCA Manual N for commercial load calculations. We may add commercial support in a future update.
How do I convert BTU to tons?
Divide the total BTU by 12,000. One ton of cooling capacity equals 12,000 BTU per hour. So if your calculated load is 36,000 BTU/h, you need a 3-ton system (36,000 ÷ 12,000 = 3). Standard residential AC units come in half-ton increments: 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, and 5 tons. Always pick the nearest standard size; rounding up by more than half a ton means you’re oversizing.