It’s 2:47 PM on a Tuesday. Your HVAC team has six technicians running full schedules, every slot is confirmed, and every customer expects their technician on time.
Then the call comes in: “No heat, house is 28°F, elderly resident.” This is a P0 emergency.
You need a tech there within 90 minutes. But everyone’s booked. What happens next?
If you’re using a traditional dispatching system, you’re about to spend the next 20 minutes juggling phone calls, checking schedules, and making impossible trade-offs. Cancel a confirmed appointment? Force overtime? Delay the emergency and hope nothing bad happens?
AI dispatching eliminates this scramble.
Emergency job handling in AI dispatch is an automated process where the system detects high-priority service calls, evaluates all available technicians, and assigns the optimal response within seconds. Without manual reshuffling and promises to existing customers.
In FieldCamp’s AI dispatch software, a gas leak or no-heat call triggers immediate technician evaluation based on proximity, skills, current workload, and SLA risk. The system adjusts schedules automatically while preserving every confirmed customer commitment.
This guide breaks down exactly how AI dispatching systems detect emergencies, evaluate response options, insert urgent jobs without breaking commitments, and communicate changes to everyone involved, automatically.
Prefer listening instead?
How AI Detects Emergency Calls in Seconds?
When an emergency call arrives, every second matters. AI dispatching systems identify and classify these urgent service requests instantly, triggering the appropriate response protocol before a human dispatcher could even pull up the schedule.
What the AI Reads Immediately
The moment a new job enters the system, whether from a ServiceTitan integration, manual entry, or customer call, the AI scans critical data points:
- Priority flag: Is this marked as emergency, urgent, or routine?
- Job type: What category of work does this require?
- Customer notes: Are there keywords like “no heat,” “gas smell,” or “flooding”?
- Time window: Does the customer need same-day or immediate service?
The Priority Classification System
AI dispatching uses a tiered priority system to determine response urgency:
| Priority | Label | Description | Scheduling Behavior |
| P0 | Emergency | Life, safety, or property damage | Schedule immediately, optimize for speed |
| P1 | Urgent | Important, needs same-day attention | Schedule early in the route |
| P2 | High | Standard high-priority work | Normal scheduling |
| P3 | Normal | Routine service requests | Default scheduling |
| P4 | Low | Non-urgent, maintenance | Fills remaining capacity |

Industry-Specific Emergency Triggers
Different trades define emergencies differently. What counts as P0 for an HVAC company isn’t the same as a plumbing business or electrical contractor.
HVAC Emergencies:
- No heat when the outdoor temperature drops below 32°F
- No AC when outdoor temperature exceeds 100°F
- Gas furnace smell or carbon monoxide alarm activation
Plumbing Emergencies:
- Gas leak detection
- Sewer backup into the home
- Burst pipe causing active flooding
- Complete loss of water to the property
Electrical Emergencies:
- Complete power outage
- Sparking outlets or a burning smell
- Exposed live wires
- Electrical panel smoking or overheating
The Detection Sequence
Here’s how the detection process unfolds, in milliseconds:
1. Job data ingestion: AI reads incoming job information
2. Priority flag check: System identifies P0/P1 markers
3. Trigger word scan: Notes are scanned for emergency keywords
4. Cross-reference: Job type + priority + time sensitivity evaluated together
5. Response protocol activation: Emergency handling sequence begins
Example: A “no heat” call arrives at 2 PM. The outdoor temperature is 28°F, and the customer is elderly. The AI immediately flags this as P0, triggering the emergency response protocol without human intervention required.
FieldCamp’s AI dispatcher evaluates emergency calls in seconds, compared to several minutes for manual dispatchers juggling schedules and phone calls.
For more on how priority levels influence the broader scheduling system, see our guide to How AI Dispatching Thinks.
The Emergency Evaluation Matrix: How AI Picks the Right Technician
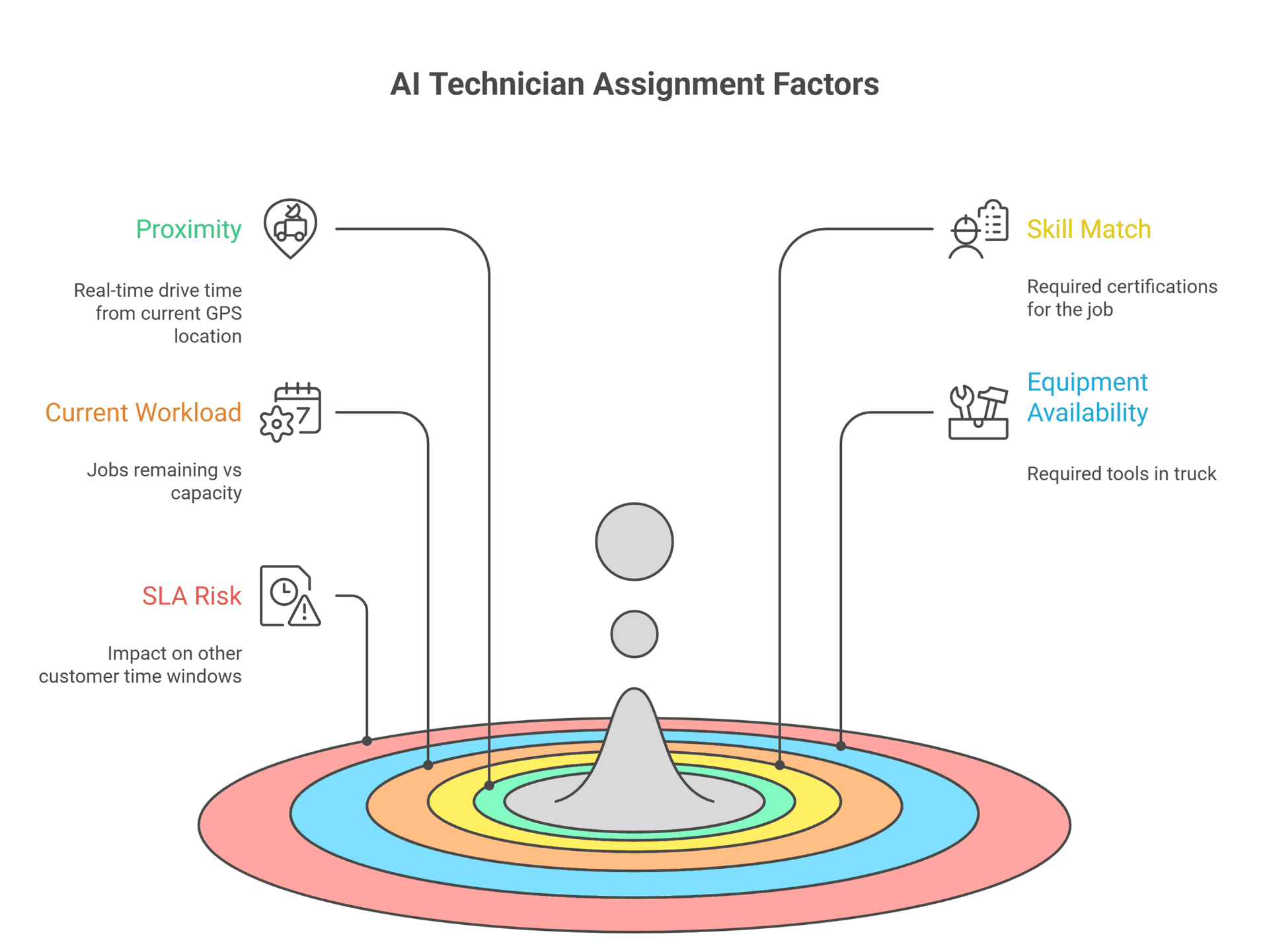
Once an emergency is detected, the AI evaluates all available technicians across five dimensions simultaneously. This isn’t a simple “who’s closest” calculation; it’s a weighted scoring system that balances speed, qualifications, and downstream impact.
Five-Factor Scoring System
| Evaluation Factor | Weight (for P0) | What It Measures |
| Proximity | High | Real-time drive time from the current GPS location |
| Skill Match | Critical (hard constraint) | Required certifications for the job |
| Current Workload | Medium | Jobs remaining vs. capacity |
| Equipment Availability | Medium | Required tools in the truck vs. at the depot |
| SLA Risk | High | Will this cause other customers to miss windows? |
Proximity Score: The AI calculates real-time drive time from each tech’s current GPS location, not their last scheduled stop. This matters because a technician who finished early is in a different place than the schedule shows.
Skill Match: For emergencies involving gas lines, high voltage, or specialized equipment, this becomes an absolute requirement. The system won’t send an unqualified technician regardless of proximity.
Learn more about how this works in our skills-based technician assignment guide.
Current Workload: A technician with two jobs left has more flexibility than one with five. The AI factors this into assignment decisions to maintain balanced team workloads.
Equipment Availability: A sewer backup requires a camera. A furnace repair needs diagnostic tools. The AI knows what’s in each truck.
SLA Risk: Before making any assignment, the AI calculates the downstream impact. Will pulling this tech cause another customer to miss their window?
When Proximity Doesn’t Win?
For P0 emergencies, AI prioritizes response time over route optimization. The system will accept a slightly longer total drive time across the day if it means getting a technician on-site faster.
But there’s one scenario where proximity doesn’t win: when the emergency requires specialized certification.
Example: A plumbing company receives a gas leak call. Tech A is 8 minutes away but lacks gas-line certification. Tech B is 22 minutes away but has the required certification. The AI assigns Tech B despite the longer drive time, because sending an unqualified technician to a gas leak isn’t just inefficient; it’s dangerous and potentially illegal.
The AI runs this evaluation matrix across ALL available technicians simultaneously, producing a ranked list of options in milliseconds.
Protected Appointment Logic: How AI Inserts Emergencies Without Breaking Promises
Here’s the core problem with emergency dispatching: you need to fit an urgent job into a full schedule without destroying customer trust. Cancel a confirmed appointment, and you’ve damaged a relationship. Delay the emergency, and you’ve created a safety risk.
AI dispatching solves this through protected appointment logic.
What Is Protected Appointment Logic?
Protected appointment logic is the constraint system that treats confirmed (pinned) appointments as immovable anchors during emergency insertions. When a P0 emergency arrives, the AI will only insert it into time slots that don’t displace appointments customers have already confirmed.
This is a hard constraint, meaning the system will never violate it, even for life-safety emergencies. If no insertion is possible without breaking a confirmed commitment, the AI flags the situation for dispatcher override rather than making a decision that breaks customer trust.
Protected appointment logic is one example of a hard constraint, rules the AI will never break, regardless of circumstances. Other scheduling preferences, like technician route efficiency or preferred time slots, function as soft constraints that the system can bend when necessary.
Understanding this hierarchy explains why the AI makes certain trade-offs during emergency insertion. For a deeper look at how these constraint types interact, see our guide to Hard Constraints vs. Soft Constraints.
The Four Emergency Insertion Strategies
When an emergency arrives, the AI evaluates multiple insertion strategies before selecting the best option:
1. Gap Insertion The AI identifies existing gaps in the schedule, travel time buffers, planned breaks, or natural spacing between jobs, and slots the emergency into that space without any other appointments’ move.
2. Planned Job Displacement Appointments that haven’t been confirmed with the customer (status: PLANNED) can be moved to later slots or rescheduled for the next day. Confirmed appointments never move. This is why job status management matters so much for dispatch efficiency.
3. Route Resequencing Sometimes the solution isn’t adding time, it’s rearranging the order of existing jobs to create a window for the emergency without extending the day. The AI can reorder stops to open a slot. See how this connects to AI route optimization.
4. Overflow to Next Available Tech If the primary candidate’s schedule is fully pinned with confirmed appointments, the AI moves to the next-best technician option from the ranked list.

Emergency Insertion in Action
Before the emergency arrives:
Tech 1’s schedule: 9 AM (confirmed), 11 AM (planned), 2 PM (confirmed), 4 PM (planned)
Emergency arrives at 10 AM:
P0 call needs a response by 11:30 AM
AI solution:
- Insert an emergency at the 11 AM slot
- Move the planned 11 AM job to the 3 PM slot
- Keep both confirmed appointments (9 AM and 2 PM) unchanged
The customer who had the 11 AM planned appointment receives a notification about the time change. Both confirmed appointments proceed exactly as promised.

The Hard Rule
The system NEVER displaces confirmed appointments. P0 emergencies are no exception.
If no insertion is possible without breaking a confirmed commitment, the AI flags the situation for dispatcher review, presenting options rather than making a decision that breaks trust with an existing customer.
In practice, most emergency insertions happen without displacing any confirmed appointments. The combination of gap insertion, planned job displacement, and route resequencing handles the vast majority of scenarios.
For more on how AI reshuffles schedules after emergency insertion, see our guide to Dynamic Rerouting: When Plans Change.
Real-Time Customer Communication During Emergency Response
When the AI inserts an emergency and adjusts the schedule, it triggers a cascade of automated customer communications. Nobody gets left wondering where their technician is.
The Automated Notification Sequence
1. Emergency Customer Notification The customer who called with the emergency receives immediate confirmation: “Tech assigned, ETA 22 minutes.” This happens within seconds of the AI making the assignment.
2. Displaced Planned Appointment Notification Any customer whose planned (not confirmed) appointment was moved receives a text or email: “Your 11 AM appointment has been moved to 3 PM due to an emergency. Reply YES to confirm or CALL to reschedule.”
3. Downstream ETA Updates If route changes affect arrival times for other customers, they receive updated ETAs automatically. No manual calls required.
Customer Response Handling
The notification system isn’t one-way. Customers can respond:
- Confirm: Customer replies YES, and the AI locks in the new time
- Reject: Customer indicates the new time doesn’t work, and the AI re-evaluates to find an alternative
- Call: Customer wants to discuss options with a human
Dispatcher Visibility
While all this happens automatically, the dispatcher isn’t left in the dark. The real-time dispatch dashboard shows:
- All schedule changes as they happen
- Customer notification status (sent, confirmed, pending)
- Any situations requiring human intervention
- Override options if the dispatcher wants to make manual adjustments
Example Communication Flow
| Time | Event |
| 10:02:00 AM | Emergency call logged (gas leak, P0) |
| 10:02:03 AM | AI assigns Tech 2, inserts an emergency at 10:30 AM |
| 10:02:05 AM | Emergency customer receives: “Technician Mike is on his way. ETA: 28 minutes.” |
| 10:02:08 AM | Customer A (originally 10:30 AM, planned) receives: “Your appointment has been moved to 2:00 PM. Reply YES to confirm.” |
| 10:04:00 AM | Customer A replies YES |
| 10:04:01 AM | AI locks new time, updates route, recalculates all downstream ETAs |
Total time from emergency call to full schedule adjustment with customer notifications: under 2 minutes.

Industry-Specific Emergency Patterns and Classification
Emergency classification varies by trade and conditions.
Getting this right matters; misclassifying a P1 as P0 wastes emergency buffer capacity. Misclassifying a P0 as P1 creates liability exposure and customer safety risks.
Emergency Classification by Trade
| Trade | Priority | Trigger Conditions | Target Response |
| HVAC | P0 | No heat (outdoor temp below 32°F) | 90 min |
| HVAC | P0 | No AC (outdoor temp above 100°F) | 90 min |
| HVAC | P0 | Gas furnace smell / CO alarm | 60 min |
| HVAC | P1 | System failure (moderate weather) | Same-day |
| Plumbing | P0 | Gas leak | 60 min |
| Plumbing | P0 | Sewer backup into the home | 90 min |
| Plumbing | P0 | Burst pipe with active flooding | 60 min |
| Plumbing | P1 | Water heater failure | Same-day |
| Electrical | P0 | Complete power outage | 90 min |
| Electrical | P0 | Sparking/burning smell | 60 min |
| Electrical | P0 | Exposed live wires | 60 min |
| Electrical | P1 | Partial outage (critical circuits) | Same-day |
Seasonal and Geographic Variations
Emergency patterns shift with seasons and locations:
- Winter surge: HVAC companies see “no heat” emergencies spike when temperatures drop
- Freeze season: Plumbing emergencies related to burst pipes cluster during cold snaps
- Storm damage: Electrical emergencies increase after severe weather events
- Heat waves: AC emergencies become P0 when temperatures exceed safe thresholds
Geographic context matters too. A “no heat” call in Phoenix in January might be P2. The same call in Minneapolis is P0. Smart AI dispatching systems account for local weather conditions when classifying urgency.
Misclassifying emergencies doesn’t just create liability risks; it also burns out your team. When every call gets treated as P0, technicians end up running ragged through unpredictable schedules, overtime becomes the norm, and your best people start looking elsewhere.
Proper emergency classification protects both customers and your workforce. Learn how smart dispatching keeps workloads sustainable in our guide to Preventing Technician Burnout.
The Emergency Buffer Strategy: Planning for the Unexpected
Smart field service operations don’t just react to emergencies; they plan for them. Emergency buffer strategy is the capacity planning practice where companies reserve 15–20% of daily technician capacity specifically for unexpected P0/P1 calls.
How Buffer Capacity Works
The AI doesn’t just leave random gaps. It strategically manages buffer time:
- Morning/midday priority: Fill earlier slots first, keeping afternoon flexibility
- End-of-day windows: Reserve the 3–5 PM window as primary emergency buffer
- Flexible until late afternoon: Buffer slots remain available until it’s clear they won’t be needed
- Automatic overflow: If no emergencies arrive, buffer time gets filled with next-day jobs pulled forward
Seasonal Buffer Adjustments
Buffer strategy isn’t static. During peak emergency seasons, smart companies increase their reserve:
| Season | Recommended Buffer |
| Standard operations | 15–20% of daily capacity |
| Peak season (summer/winter) | 25–30% of daily capacity |
| HVAC during temperature extremes | Higher buffer for climate emergencies |
| Plumbing during freeze season | Increased buffer for burst pipe calls |
The Trade-Off (And Why It’s Worth It)
Yes, emergency buffers mean slightly fewer scheduled jobs per day. But the math works in your favor:
Without a buffer strategy:
- Emergencies force overtime (expensive)
- Confirmed appointments get canceled (customer trust damaged)
- Dispatchers spend hours manually reshuffling (productivity lost)
- Next-day overflow creates scheduling debt
With buffer strategy:
- Emergencies absorbed without overtime
- Confirmed appointments protected
- AI handles insertion automatically
- Schedule remains stable day over day
Real-world example: An HVAC company with 5 technicians reserves 4–6 PM slots as an emergency buffer. During a July heat wave, they handled 12 same-day AC emergencies across 3 days without overtime or cancellations. Without a buffer strategy, 8 of those 12 would have required overtime or next-day scheduling.
Multi-Emergency Cascade Scenarios: When It All Hits at Once
During peak seasons, many service days include two or more simultaneous emergencies. Manual dispatchers facing multiple emergencies often resort to triage by gut instinct, potentially missing optimal solutions or creating downstream problems.
AI handles cascade scenarios systematically.
How AI Handles Multiple Simultaneous Emergencies?
Step 1: First Emergency (2:15 PM)
- No-heat call arrives (P0)
- AI evaluates all technicians
- Tech 3 assigned, arrives 2:52 PM
Step 2: Second Emergency (2:40 PM)
- Gas leak reported (P0)
- AI re-evaluates remaining technicians (excluding Tech 3)
- Tech 1 assigned, arrives 3:05 PM
Step 3: Third Emergency (3:10 PM)
- Sewer backup call (P0)
- All primary techs are committed
- AI presents options to the dispatcher:
- (a) Call the backup technician
- (b) Move the planned 4 PM job to tomorrow
- (c) Authorize overtime for Tech 5

Priority Triage Within Emergencies
When multiple P0 calls arrive simultaneously, the AI ranks by severity:
1. Life-safety emergencies first: Gas leaks, carbon monoxide, exposed electrical
2. Property damage second: Active flooding, burst pipes
3. Service disruption third: No heat/AC, power outage
Overflow Handling
When capacity is truly exceeded, the AI doesn’t fail silently. It flags the situation and presents clear options:
- Backup tech available: “Call in backup technician for $X overtime cost.”
- Planned job moveable: “Reschedule Johnson 4 PM to tomorrow, customer not yet confirmed.”
- Overtime authorization: “Extend Tech 5’s shift by 2 hours to cover.”
The dispatcher makes the final call, but the AI has already done the analysis and math.
Emergency insertions don’t happen in isolation; they ripple through the entire day’s schedule. When the AI slots a P0 call into Tech 3’s route, it simultaneously recalculates arrival windows for every downstream customer.
The goal isn’t just to handle the emergency; it’s to ensure that Mrs. Johnson’s 4 PM appointment still falls within her confirmed 3:30–4:30 PM window, even after the schedule shift. This precision is what separates AI dispatching from manual reshuffling, where downstream time windows often get sacrificed in the scramble.
For a detailed breakdown of how the system protects these commitments, see our guide to Time Window Optimization.
How FieldCamp Handles Emergency Job Insertion?
When that 2:47 PM no-heat call arrives, here’s what FieldCamp does in seconds:
1. Detects P0 priority from “no heat” + 28°F + elderly resident
2. Evaluates all 6 technicians for EPA certification + proximity + workload
3. Assigns Tech #3 (certified, 18 min away, 3 jobs remaining)
4. Moves Tech #3’s 4 PM planned job to Tech #5’s open slot
5. Sends customer ETA notification: “Tech arriving 3:25 PM”
Priority-Based Detection
FieldCamp’s priority-based dispatching automatically detects P0/P1 jobs from ServiceTitan integration or manual entry. The moment an emergency job enters the system, the AI recognizes its priority level and triggers the appropriate response protocol.
Real-Time Technician Evaluation
Using GPS data from technician mobile devices, FieldCamp calculates accurate emergency response times based on the actual current location, not the last scheduled stop. This means the “closest available tech” calculation reflects reality, not assumptions.
Protected Appointment System
FieldCamp’s pinning system ensures confirmed jobs never move, even for emergencies. When a customer confirms their appointment, that time slot becomes an immovable anchor. The AI works around these anchors, finding creative solutions rather than breaking promises.
Automatic Customer Notifications
Within seconds of any schedule change, affected customers receive notifications. Emergency customers get ETA confirmations. Displaced planned appointments get rescheduling options. Downstream customers get updated arrival windows.
These notifications aren’t generic messages; they’re triggered by specific workflow events and designed for each customer’s situation. A customer whose planned appointment moved gets different messaging than one whose ETA shifted by 15 minutes.
FieldCamp’s workflow automation handles this automatically, ensuring every affected customer receives timely, relevant updates without dispatcher intervention. See how this works in practice with our Real-Time Customer Service Updates workflow template.
What Makes FieldCamp Different?
1. Speed: FieldCamp evaluates and assigns emergencies in seconds, compared to several minutes for manual dispatching.
2. Intelligence: Unlike basic field service scheduling software that requires manual reshuffling, FieldCamp’s AI automatically finds the optimal insertion point, balancing response time, technician qualifications, and schedule impact.
3. Learning: The system learns your typical emergency volume and suggests optimal buffer capacity based on historical patterns. Over time, it gets smarter about predicting when and where emergencies are likely to occur.
You’re Still Dispatching Like It’s 2018
Phone calls. Gut decisions. Apologizing to customers. The companies eating your lunch have automated this already.
Conclusion
When that 2:47 PM no-heat call arrives, FieldCamp’s AI evaluates all technicians, protects existing appointments, and assigns the optimal response in seconds, not the several minutes manual dispatching requires. The system handles single emergencies and multi-emergency cascades with the same speed and accuracy.
The protected appointment logic, automated customer communication, and real-time technician evaluation solve what used to be a dispatcher’s worst nightmare. Whether it’s one emergency or three arriving simultaneously, the system evaluates every option, protects existing commitments, and finds the optimal response.
Understanding emergency handling is just one piece of AI dispatching. To see how the system manages the broader constraint hierarchy that makes this possible, read How AI Dispatching Thinks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if an emergency arrives when all technicians are fully booked with confirmed appointments?
FieldCamp evaluates three options: identify the earliest flexible time slot after current commitments, check if any jobs can be completed faster to create a gap, or flag for the dispatcher to authorize overtime. The system never cancels confirmed appointments, even for P0 emergencies.
How does AI decide which technician to send to an emergency when multiple techs are available?
The AI runs a five-factor evaluation: proximity to the emergency site, required skill/certification match, current workload, equipment availability, and SLA risk to other customers. For P0 emergencies, proximity and skills are weighted highest.
Can AI dispatching handle multiple emergencies arriving at the same time?
Yes. When multiple emergencies arrive within minutes, the AI evaluates each against all available technicians simultaneously, assigns the best match for each emergency, and rebalances the remaining schedule. If capacity is exceeded, the system flags for dispatcher intervention.
How long does it take for AI to assign a technician to an emergency call?
FieldCamp’s AI dispatcher completes emergency evaluation and assignment in seconds, including technician scoring, schedule insertion, route recalculation, and customer notification triggers.
What’s the difference between how AI handles a P0 vs a P1 emergency?
P0 emergencies trigger immediate response, where AI prioritizes speed over route optimization. P1 emergencies are balanced against route efficiency and may be scheduled for the next available optimal slot rather than immediate insertion.
What job statuses does the system recognize?
FieldCamp recognizes five statuses: PLANNED (can be moved), CONFIRMED (pinned, won’t move), IN_PROGRESS (pinned, technician, working), COMPLETED (finished), and CANCELLED (removed from schedule). Only PLANNED jobs can be displaced during emergency insertion.

