AI dispatcher algorithms work by combining routing optimization (VRP), rule-based constraint programming, machine learning predictions, and real-time re-optimization to automatically assign the right technician to the right job at the right time.
In 2026, modern AI dispatching systems continuously evaluate technician availability, skills, job complexity, live traffic, SLAs, and business rules to generate and adjust schedules in seconds—something human dispatchers cannot calculate at scale.
This doesn’t happen on its own. Behind every optimized schedule are specialized algorithms that calculate routes, enforce operational rules, predict outcomes, and react to changes in real time. These algorithms work together to decide who should do which job, in what order, and at what time—while keeping the rest of the day intact.
Once feasibility is confirmed, dispatchers can manually or automatically assign jobs to technicians when needed.
Together, these algorithms form the decision engine behind AI dispatching. This guide breaks down how each layer works, so you can see exactly how AI manages complexity at scale and keeps field service schedules running smoothly.
Let’s get started.
What Are AI Dispatcher Algorithms?
AI dispatcher algorithms are automated decision systems that evaluate jobs, technicians, constraints, and live conditions to generate optimal schedules in real time. They replace manual guesswork with fast mathematical and predictive models that continuously adapt as the day changes.
Previously, dispatching used to be mostly intuition: matching the right tech to the right job, trying to reduce drive time, adjusting when emergencies popped up, and hoping the day didn’t fall apart at 3 PM.
But modern field service operations are too complex for guesswork. AI dispatcher algorithms exist because no human can juggle hundreds of moving parts at once — skills, locations, delays, traffic, SLAs, and workload balance — all evolving in real time.
The AI dispatcher algorithms are your ultra-fast planning engine. They evaluate everything happening in your day and build the smartest possible schedule.
This shift is part of a broader move toward field service automation, where systems make operational decisions in real time.
Here’s what the AI actually looks at:
- Every job request and its true complexity
- Every technician’s skills, availability, location, and past performance
- Customer time windows and promised ETAs
- Live traffic conditions and travel predictions
- Priorities like emergencies, VIPs, warranties, or recurring contracts
- Business rules — no overtime, territory boundaries, SLAs, etc.
These factors help the system evaluate millions of possible technician–job combinations in under a second. That’s how it finds the best match for each job without breaking the rest of the day.
One thing to note that these decisions depend heavily on how accurately technician skills are defined, which is why teams first set up technician skills and certifications inside the system.
Why Dispatching Needs Algorithms?
Dispatching needs algorithms because modern field service operations generate more variables than humans can process accurately in real time. AI handles complexity by simulating downstream impacts, recalculating ETAs, and preventing small delays from cascading into full-day failures.
A human dispatcher typically handles 10–20 variables at a time. While, a field service operation produces 200–400+ variables every hour.
If you’re curious how dispatching became this complex over the years, our evolution of AI dispatching guide breaks down the entire journey, from paper boards to today’s algorithm-driven operations.
Let’s continue with what overwhelms humans—and what algorithms handle in seconds:
1. Job Complexity
Each job has unique requirements: duration, skills, risk level, time window (AI compares thousands of sequencing possibilities instantly.)
2. Technician Variability
Every tech works differently: speed, expertise, familiarity with certain brands (AI predicts which tech will complete each job fastest and most accurately.)
3. Traffic & ETA Shifts
Traffic changes constantly (AI recalculates ETA impact before small delays become big problems.)
4. Downstream Delay Impact
One late job can disrupt the next 3–5 (AI simulates ripple effects and rearranges proactively.)
5. Customer Preferences
Some customers prefer the same technician, earliest slot, or VIP priority (AI remembers these patterns for you.)
6. Compliance, Breaks & Overtime
Labor laws and internal rules are easy to break
(AI analyzes every rule before suggesting a schedule.)
Types of Algorithms Used in AI Dispatching
AI dispatching systems rely on multiple algorithm types working together rather than a single model. It’s a combination of four core systems working together; routing optimization, constraint programming, machine learning, and real-time solvers. Each solves a different operational problem.
Let’s understand them in-depth;
The Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP): Core Engine of AI Dispatching
VRP is the mathematical backbone of dispatch optimization. If AI dispatcher algorithms are the “brain,” VRP is the logic system that controls how that brain builds efficient routes.
Every field service business, whether they realize it or not, runs into VRP every single day.
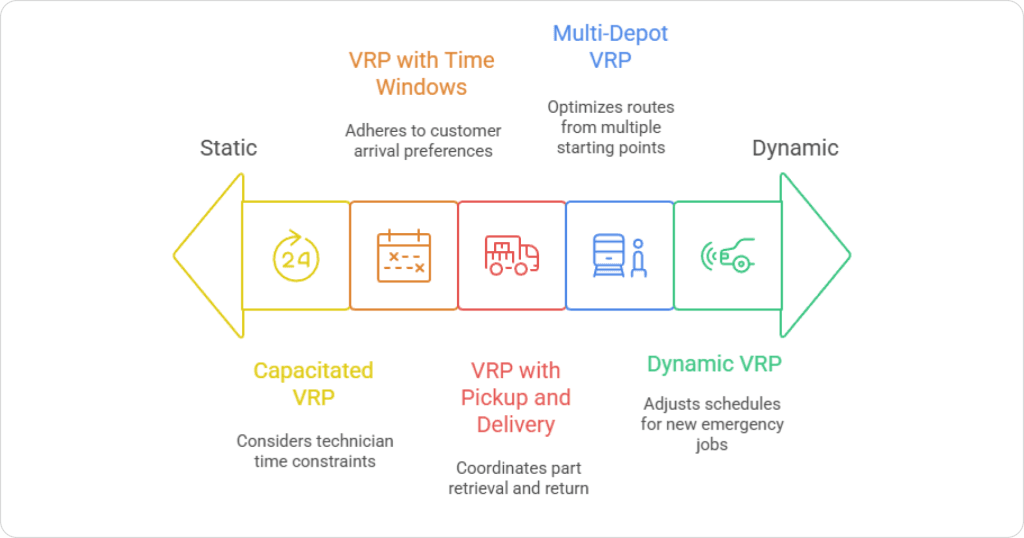
What Does VRP Actually Mean?
The Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) is the mathematical foundation that determines the most efficient way for technicians to complete jobs while respecting real-world constraints.
At its core, VRP answers a simple question:
“What’s the most efficient way for multiple technicians to complete multiple jobs while obeying all rules and constraints?”
To solve that, VRP must consider:
- Number of technicians
- Number of jobs
- Job locations
- Travel times
- Technician capacity (hours, skills, zones)
- Job time windows
- Priority levels
- Real-time disruptions
Types of VRP Variants in Field Service
Real operations rarely match a “simple” version of VRP. Your business is usually dealing with several variations at once:
- CVRP (Capacity-Constrained VRP)
Limits based on working hours, fatigue, tools, vehicles, and skills. - VRPTW (VRP with Time Windows)
Jobs must happen within customer or SLA windows (e.g., 8–10 AM). - DVRP (Dynamic VRP)
When traffic changes, jobs cancel, techs run late — routes must adapt live. - MVRP (Multi-Depot VRP)
Technicians starting from different depots, offices, or home locations.
Why VRP Matters for Your Schedule?
VRP matters because route optimization complexity grows exponentially as jobs increase, making manual planning mathematically impossible beyond a small scale.
Every time you try to plan the day, VRP is happening — you’re just doing it manually.
The catch: humans can’t compute optimal routes because VRP grows exponentially:
- 10 jobs → 3.6 million possible route combinations
- 20 jobs → 2.4 quintillion possibilities
- 50+ jobs → more possibilities than you could explore in a lifetime
So dispatchers naturally fall back to simple rules:
- “Send whoever is closest.”
- “Give all north-side jobs to Mike.”
- “Drop emergencies on whoever frees up first.”
It works until it doesn’t.
FieldCamp’s VRP Engine
FieldCamp uses a hybrid VRP approach (Google OR-Tools + Timefold) to:
- Generate efficient routes
- Handle time windows and SLAs
- Respect shifts and breaks
- Reduce travel cost and deadhead miles
- Maintain job order and dependencies
- Re-optimize quickly when disruptions hit
The result: optimized routes that human dispatchers simply cannot calculate at scale in seconds.
Constraint Programming: Making AI Respect Real-World Rules
Constraint programming ensures AI-generated schedules are operationally valid, compliant, and realistic—not just mathematically efficient.
Scheduling is not only about efficiency — it’s about honoring the rules that make your operation workable.
Constraint programming makes sure the algorithm follows your business logic instead of breaking it for a mathematically “perfect” but impossible schedule.
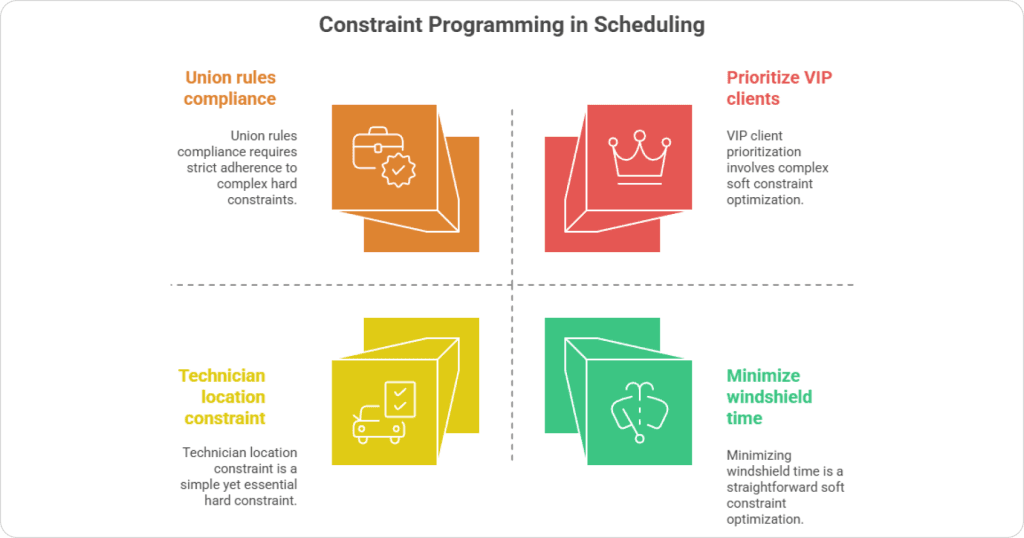
Hard Constraints (Non-Negotiable Rules)
Hard constraints define rules that the AI can never violate, ensuring legal, safety, and feasibility compliance.
These must never be violated:
- A technician must have the required skills and certifications
- Jobs must happen within the promised time window
- No overlapping jobs for a tech
- Tech shift boundaries cannot be broken (unless explicitly allowed)
- Territory or zone restrictions must be respected
These rules ensure the schedule never produces impossible or non-compliant assignments.
To avoid cross-zone assignments, many teams configure territory restrictions at the technician or job level.
Soft Constraints (Preferences the AI Tries to Honor)
Soft constraints influence schedule quality by optimizing preferences like reduced drive time, workload balance, and technician familiarity.
These can be bent when needed, but the AI tries to satisfy them as much as possible:
- Minimize total drive time
- Reduce overtime
- Prefer familiar technicians for repeat customers
- Avoid long idle gaps between jobs
- Balance workload across the team
- Assign top performers to complex or high-value jobs
Soft constraints shape how good the schedule feels — for customers, techs, and the business.
Why Constraint Programming Is Essential?
If VRP is “how to build a route,” constraints control “how the route should behave.”
Without constraints, optimization would be mathematically clean but operationally useless — like sending an unlicensed tech to a gas furnace job just because they’re close.
FieldCamp’s Constraint Engine
FieldCamp lets businesses customize rules such as:
- Maximum drive time per zone or region
- Skill-based routing and certifications
- Customer preference matching
- Overtime and max-hours limits
- Day-of-week rules (e.g., no long jobs on Fridays)
- Technician home-routing at the end of the day
That means the AI behaves like your business, not like a generic solver.
Machine Learning: The Brain That Learns From Your Jobs
Machine learning enables AI dispatching systems to improve accuracy over time by learning from historical job outcomes and dispatcher behavior.
VRP and constraint programming help the system calculate optimal schedules.
Machine learning (ML) helps it predict how your real world will behave.
Where routing engines focus on where jobs should go, ML focuses on:
- How long jobs will actually take
- Which technician is most suitable beyond just skills
- Which jobs are likely to run late
- Which customers or job types tend to create extra work
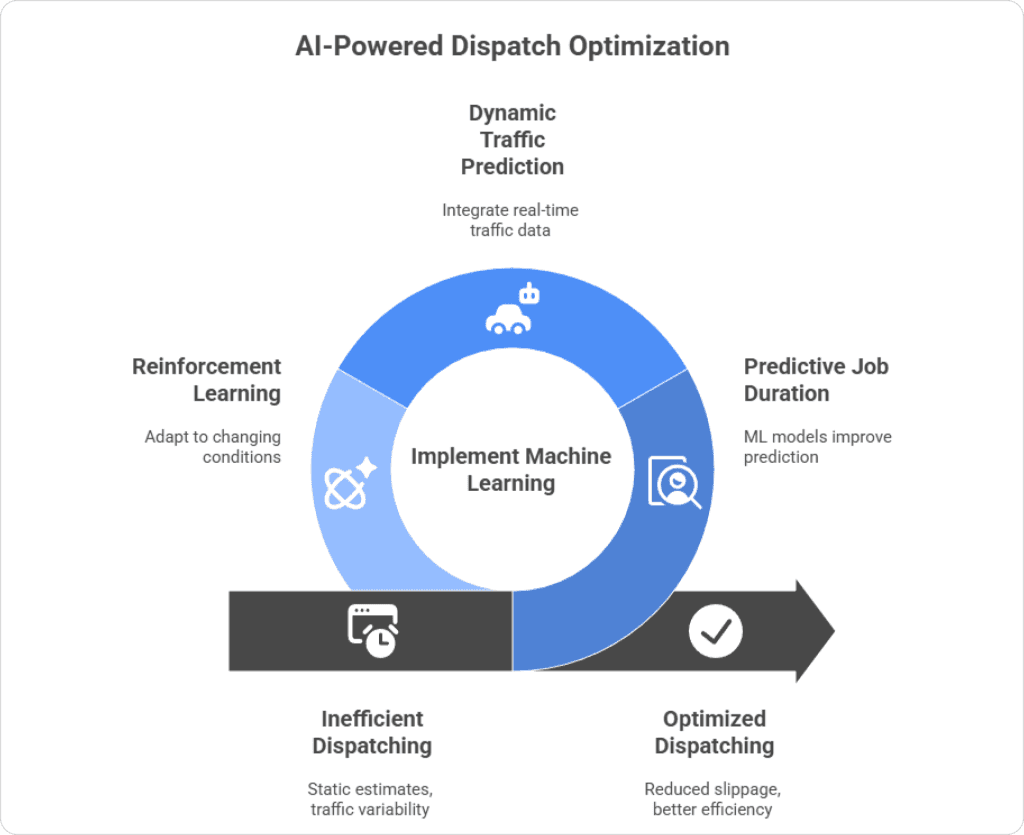
Why ML Matters in Dispatching?
ML matters because it replaces static estimates with predictive insights based on real operational patterns.
Field operations live in uncertainty:
- Job duration varies by technician and situation
- Traffic changes day to day
- Some customers always take longer (questions, approvals, access issues)
- Certain job types usually require follow-up visits
- Busy seasons stretch everything — HVAC in summer/winter, for example
ML models detect patterns across thousands of past jobs and then:
- Predict realistic job durations instead of using flat estimates
- Highlight which tech is more efficient for specific job types
- Improve schedule density without increasing overtime risk
- Learn from dispatcher overrides and adjust future recommendations
In short: the more you use the system, the smarter it gets.
How FieldCamp Uses ML?
FieldCamp’s ML layer helps:
- Predict job duration per technician and job type
- Improve travel time estimates using historical patterns, not just current traffic
- Recognize seasonal workload changes
- Adjust for repeat-customer quirks (slow payers, always-late access, etc.)
- Estimate first-time fix probability to avoid unnecessary revisits
This is how your dispatcher goes from “educated guesses” to data-backed decisions without having to run reports all day.
Real-Time Optimization: How AI Reacts When the Day Falls Apart
Even the best-planned schedule collapses the moment real life shows up.
- A technician runs late
- Traffic spikes unexpectedly
- A customer cancels without warning
- An emergency request arrives at 3:17 PM
- A “simple” job turns into a 2-hour diagnostic nightmare
Traditional dispatching simply cannot keep up with this level of unpredictability.
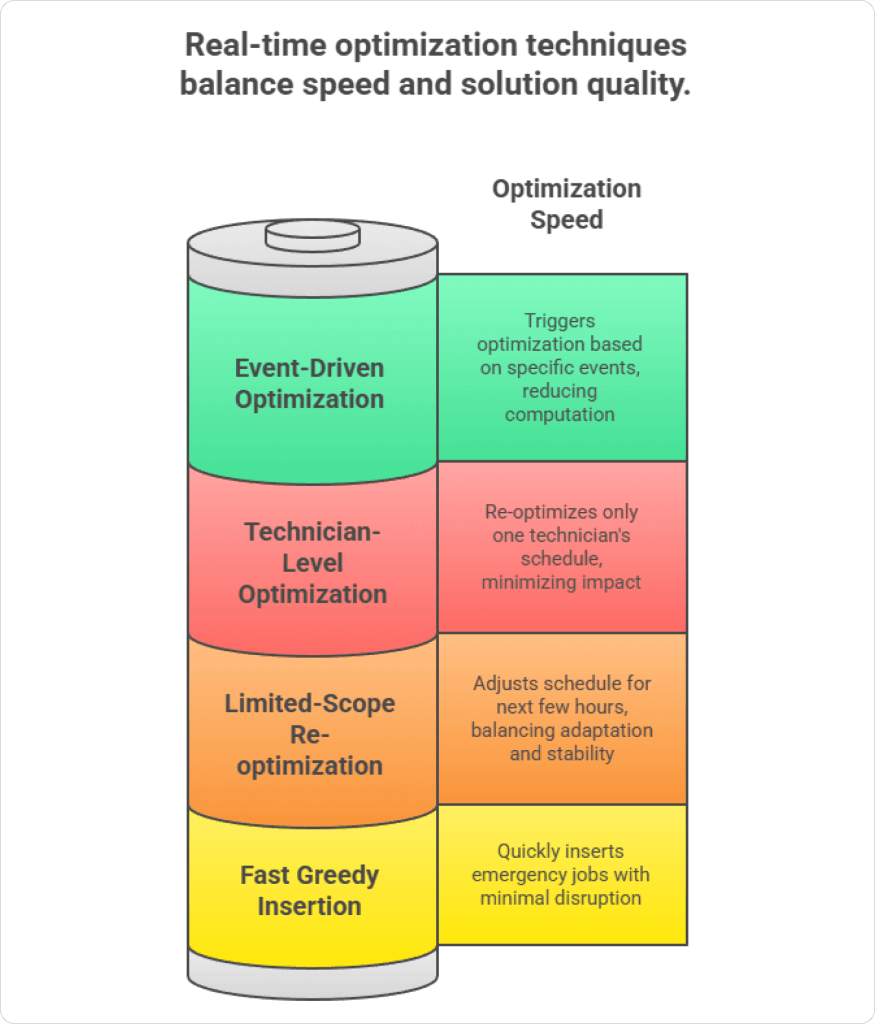
Even the most experienced dispatcher can’t manually re-evaluate every route, every ETA, every SLA promise, and every downstream impact in real time.
This is where real-time optimization becomes the heart of AI dispatching — especially inside FieldCamp.
Real-time optimization isn’t about “reshuffling jobs quickly.” It’s about continuously recalculating the entire operational puzzle without breaking the flow of the day.
However, these constraints work only when job time windows are defined correctly, which is why teams configure service time windows at the job level.
What Real-Time Optimization Actually Does?
Real-time optimization is a continuous decision loop that monitors:
- Current state of every technician
- Live progress of every job
- Updated traffic predictions
- Priority changes and emergencies
- Upcoming SLA deadlines
- Delays or early completions
- Customer cancellations or reschedules
- Emerging bottlenecks and overloaded routes
Then it determines:
“What is the next best move right now that keeps today’s plan intact as much as possible?”
Think of it as a second dispatcher quietly watching everything in the background and suggesting (or automatically executing) the smartest adjustments.
How FieldCamp Handles Real-Time Optimization?
FieldCamp’s optimization engine, built for teams with 5–50 techs, blends:
- Incremental solvers – only affected routes get recalculated, not the whole day
- Fast feasibility checks – ensures suggestions are realistic and compliant
- ML-informed predictions – understands which changes are worth making
- Behavioral constraints – follows your rules, not just math
So instead of completely rebuilding the schedule and confusing everyone, FieldCamp:
- Adjusts the next few jobs for the delayed tech
- Re-routes only where needed
- Protects SLAs and VIP appointments
- Minimizes disruption for customers and technicians
Experience Intelligent Scheduling
See how FieldCamp’s AI Dispatcher builds optimized routes, prevents delays, and handles mid-day chaos automatically. Increase job capacity, improve ETAs, and eliminate manual scheduling errors for good.
How AI Dispatching Algorithms Work?
Every AI-powered dispatching system — including FieldCamp — follows the same core logic: it reads all available data, runs it through multiple optimization engines, and produces the smartest possible schedule in real time. The entire workflow can be understood in three parts: inputs, processing, and outputs.
1. Inputs: What the System Reads
The AI starts by collecting every piece of information that affects your job scheduling. For instance; job data such as the service address, the customer’s promised time window, estimated duration, required skills, and whether the job is routine, urgent, or VIP.
At the same time, it analyzes technician data — their skills, certifications, availability, current GPS location, and even historical performance patterns.
It also reads real-world conditions that impact scheduling: live traffic, technician delays, sudden cancellations, weather disruptions (if enabled), and any new job requests that come in during the day.
Finally, it considers business rules like overtime restrictions, territory boundaries, customer preferences (e.g., return tech requests), and shift policies. These inputs help the system form an accurate picture of what’s possible and what constraints must be respected.
2. Processing: What AI Does Behind the Scenes
Once the data is loaded, the algorithmic engine begins evaluating millions of potential technician–job combinations in a matter of seconds. Each component plays a specific role:
- VRP (Vehicle Routing Problem) optimizes routes and travel sequences.
- Constraint programming ensures the schedule follows real-world rules such as skills, time windows, and shift limits.
- Machine learning predicts job duration, technician speed, customer behavior, and bottlenecks before they occur.
- Real-time optimization keeps adjusting the schedule as delays, traffic, or new jobs appear.
The AI continuously runs “what if?” simulations to avoid disruption:
- What if a technician takes longer than estimated?
- What if traffic worsens on their route?
- What if the system swaps two jobs between technicians?
These micro-simulations help it settle on the lowest-cost and highest-efficiency schedule at any given moment.
3. Output: What the System Produces
After processing, the system produces an optimized version of the day — not just one that looks good but one that works in real-world conditions. It outputs the best technician schedules, perfectly sequenced routes, predicted ETAs, and alerts if any SLA is at risk. If something changes, it automatically suggests new assignments or reshuffles workloads without breaking the entire day.
A Step-by-Step Guide on How FieldCamp’s AI Dispatcher Works
Step 1: Rapid Feasibility Check (50–100 ms)
FieldCamp checks:
- Does the tech have the right skills?
- Can the job fit the time window?
- Will travel time break the schedule?
- Is a zone restriction being violated?
Impossible matches are eliminated instantly.
Step 2: Constraint-Based First Schedule (200–500 ms)
Google OR-Tools builds a valid and rule-safe schedule.
It respects:
- Time windows
- Shift hours
- Technician skill mapping
- Job dependencies
This creates a workable “skeleton schedule.”
Step 3: Deep Optimization (1–5 seconds)
Timefold (OptaPlanner) improves the schedule:
- Minimizes drive time
- Balances workload
- Reduces overtime
- Reduces backtracking
- Fixes inefficient sequences
Your schedule becomes 92–97% optimized.
Step 4: Machine Learning Enhancement (100–300 ms)
ML adjusts based on history:
- Who completes which jobs fastest
- Which zones take longer due to traffic
- Which customer always needs extra time
- Seasonal patterns
Your routes become personalized to your team.
Step 5: Real-Time Optimization (Continuous)
As soon as something changes:
- Technician delay
- Traffic spike
- New emergency job
- Customer cancellation
The algorithm reshuffles just the affected parts of the schedule.
No full rebuild.
No confusing notifications.
Just clean, surgical adjustments.
Step 6: Updated Output Delivered to All Apps
Technicians receive updated:
- Alerts
- Routes
- ETAs
- Sequence changes
Run Your Day With Real-Time AI
Let FieldCamp’s dispatcher algorithms do the heavy lifting — smart assignments, instant reshuffling, and accurate ETAs even when your day gets unpredictable.
Conclusion
AI dispatching algorithms work because they can process complexity that humans can’t handle in real time. By combining routing, constraints, learning, and live optimization, they keep schedules realistic even as traffic changes, jobs run long, or emergencies appear.
For field service teams, this means fewer reactive decisions and more control over the day. Instead of constantly fixing broken schedules, dispatchers use AI as a steady operational backbone that keeps work moving and service commitments intact.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do AI dispatching algorithms decide which technician gets a job?
They score each available technician based on skills, certifications, location, current schedule, tools on hand, and priority of the job. The algorithm then assigns the technician with the highest score, aiming for the best balance of fast response, first‑time fix, and minimal drive time.
How do AI dispatching algorithms optimize routes?
Algorithms analyze real‑time and historical traffic, job locations, appointment windows, and expected job durations. They then order visits so technicians drive the fewest kilometres while still meeting time windows and SLAs, constantly recalculating when a job runs long, cancels, or an emergency comes in.
Do AI dispatching algorithms learn from past jobs?
Manual scheduling can’t keep up with hundreds of real-time variables like traffic, delays, skills, and customer preferences. Algorithms evaluate everything at once, preventing cascading delays, missed ETAs, and overtime while improving efficiency by 20–35%.
What data does an AI dispatching algorithm need to work well?
It needs basic customer and site details, job type and priority, technician skills, calendars, service zones, and travel times. Extra data such as weather, parts availability, and historical performance helps it make smarter, more reliable scheduling decisions.

