Your dispatcher builds tomorrow’s routes. A technician calls in sick at 7 AM. Now what?
AI route optimization determines the most efficient order for your technicians to visit jobs, not just the shortest path, but the sequence that saves the most time, fuel, and headaches. It considers everything at once: who has the right skills, when customers are available, how long each job takes, and what traffic patterns look like. When something changes mid-day, it recalculates in seconds instead of forcing your dispatcher to rebuild everything manually.
The result: less driving, more jobs completed, and schedules that don’t fall apart by noon.
Most field service teams start the day with a plan. Clear routes, promised time windows, and a schedule that looks manageable.
Then reality happens.
A job runs long. Traffic slows someone down. An emergency call drops in. Suddenly, the whole routing plan starts unraveling.
This is where traditional routing hits its limit. It can map directions between two points, but it can’t adapt to real job durations, shifting ETAs, or last-minute changes.
AI route optimization solves exactly this problem. It analyzes skills, traffic, workloads, time windows, and job patterns simultaneously, building routes that stay efficient even when the day becomes unpredictable.
This guide breaks down how AI routing actually works and why it consistently outperforms manual planning in real field operations.
What Is AI Route Optimization?
AI route optimization uses algorithms to build the most efficient sequence of stops for your technicians. It’s not just picking the shortest path; it considers everything that affects a real workday: traffic patterns, job durations, technician skills, customer time windows, and workload balance.
It answers the practical question every dispatcher faces: “Who should go where, in what order, so we waste the least time and get the most done?”
Traditional routing breaks the moment something unexpected happens.
For a full breakdown of where traditional tools hit their limits, see our guide on AI Dispatching vs Traditional Dispatch Software.
AI-powered routing recalculates instantly when a job runs long, a technician is delayed, traffic spikes, or an emergency arrives. Instead of rebuilding the whole day, it adjusts only the routes that actually need fixing.
The Vehicle Routing Problem: Why This Is Harder Than It Looks
Before understanding how AI builds smarter routes, you need to know about the math problem behind all routing decisions.
The Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) is the challenge of deciding which technician should handle which jobs, in what order, while minimizing time, distance, and cost.
Sounds simple enough. But here’s why it gets complicated fast.
Why Complexity Explodes With Each Job
Routing feels easy when you have a few jobs. But every additional stop multiplies the possible combinations:
- 10 jobs = 3.6 million possible route combinations
- 20 jobs = 2.4 quintillion combinations
- 30+ jobs = more possibilities than you could evaluate in a lifetime
And that doesn’t even include real-world factors like skill matching, variable job durations, customer time windows, traffic, and urgent same-day requests.
This exponential growth explains why manual routing hits a ceiling and why algorithms become necessary as teams grow.
VRP Variations You Deal With Daily
Most teams face multiple VRP variants at once without realizing it:
Capacity-Constrained (CVRP): Technicians have limits: shift hours, tools, certifications, and travel boundaries. An HVAC tech who can install only one full system per day shouldn’t be scheduled with two.
Want to know more about CVRP? Check out our detailed guide on capacitated vehicle routing.
Time Windows (VRPTW): Most appointments aren’t flexible. A 1-3 PM job can’t move to 4:15 PM just because another job ran long.
Dynamic (DVRP): The day changes constantly. A tech falls 40 minutes behind, and the system needs to reshuffle only the affected jobs, not replan everything.
Multi-Depot (MVRP): Technicians rarely start from one location. They leave from home, branches, job sites, or storage yards. A tech on the north side shouldn’t get a south-side first job unless necessary.
These variations overlap constantly. You’re matching skills while respecting customer windows, adapting to delays, and planning across multiple start locations, all at once.
Why Human Dispatchers Can’t Keep Up
Even experienced dispatchers eventually hit a wall. Field service routing involves shifting job durations, traffic changes, technician skills, time windows, and emergency calls, all happening simultaneously.
Humans are excellent at judgment. They’re not built to evaluate thousands of combinations in real time.
The Limits of Memory-Based Routing
Dispatchers rely on fast intuition: “Send the nearest tech.” “Group these by area.” “John handles electrical, give that to him.”
These shortcuts work in simple scenarios. They can’t account for future time-window conflicts, predicted job durations, downstream bottlenecks, or workload fairness across a team.
| Factor | Human Dispatcher | AI Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Route decisions | Intuition, memory | Algorithmically optimized |
| Jobs evaluated at once | 10-15 max | Thousands |
| Time windows | Often missed | Always enforced |
| Skill matching | Memory-based | Automatic |
| Predicts downstream impact | Disrupts the entire day | Always |
| Traffic adjustments | Manual | Real-time |
| Emergency handling | Disrupts entire day | Targeted adjustments |
Hidden Costs of Manual Planning
The biggest efficiency drains aren’t immediate; they’re the ripple effects that show up hours later:
Chain reactions: One late job cascades across 3-5 downstream visits. AI predicts these impacts. Humans can’t visualize them fast enough.
Schedule collapse: A poorly sequenced route might look fine at 9 AM but fall apart by noon. AI simulates entire-day schedules before approving a route.
Overtime triggers: Early overtime creates late-day time window failures. AI monitors shift limits and adjusts routes before overtime becomes unavoidable.
Skill mismatches: They don’t hurt immediately, but they increase callbacks and reschedules later. AI prevents these misassignments upfront.
Manual routing sees the next step. AI sees the next 20 steps.
The Breaking Point
When a company scales from 3 technicians to 8, routing difficulty doesn’t double; it expands exponentially. More technicians mean more job combinations, more overlapping windows, and more zones creating cross-area travel.
Human decision-making works linearly. Routing problems expand exponentially. This mismatch creates the “breaking point” most teams feel around 6-10 technicians.
For more on dispatcher cognitive limits, see why AI dispatching matters.
How AI Route Optimization Actually Works
From the outside, AI routing looks simple: click a button, get efficient routes. Behind that simplicity is a layered decision-making system evaluating thousands of possibilities.
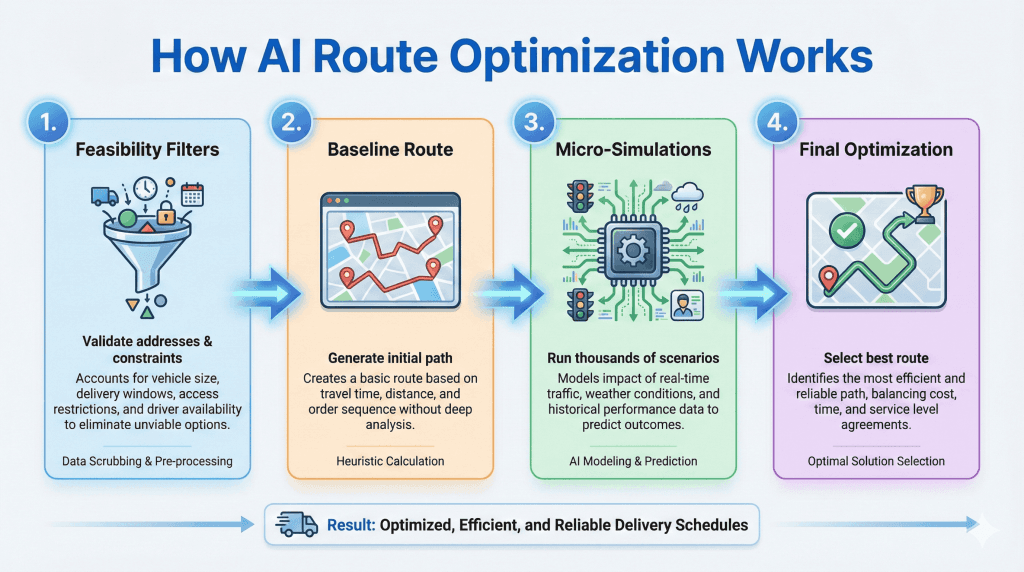
Step 1: Feasibility Filtering
AI starts by eliminating anything that would make a route impossible:
- Technician skills and certifications
- Shift hours and availability
- Job duration constraints
- Customer time windows
- Start locations and max travel range
This prevents unrealistic schedules, like assigning a 90-minute job to a 60-minute window or sending a technician across town when another is closer.
Step 2: Building a Baseline Route
Once constraints are filtered, AI builds a first draft: nearest viable jobs, time-window order, skill matches, and realistic travel times.
Humans do a version of this, too. But they typically stop here. AI uses this as a launchpad for deeper optimization.
Step 3: Running Thousands of Micro-Simulations
AI generates thousands of tiny adjustments: swapping job orders, shifting time windows, testing alternate assignments, rebalancing workloads, and reducing backtracking.
Each simulation asks: “Is there a slightly better version of this route?”
Small improvements stack up. Bad configurations get discarded instantly. Good ones become the new base for the next test.
A dispatcher might test 3-4 variations. Algorithms test thousands.
Step 4: Convergence
After enough simulation rounds, AI narrows toward the best practical route—least travel time, highest on-time probability, most balanced workload.
It doesn’t need the mathematically perfect route. It needs the best real-world route that works today.
For more on the technical systems behind this, see how AI dispatcher algorithms work.
What AI Optimizes For
Field service routing isn’t about finding the “shortest path.” A good routing engine balances competing priorities simultaneously.
Minimizing Drive Time
Every extra mile increases fuel cost, delays the next appointment, and reduces jobs completed.
AI sequences jobs to eliminate backtracking, calculates real travel time (not just map distance), and tests multiple route orders to find the most efficient flow.
Protecting Time Windows
Field service teams live and die by on-time arrivals.
AI continuously checks for time-window conflicts before they happen. It evaluates how long each job takes, how delays affect later appointments, and which jobs are at risk of slipping. If a future conflict is detected, AI reshuffles jobs in advance.
Want to know more? Check out our time window optimization guide.
Balancing Workload
Even experienced dispatchers struggle to distribute jobs fairly. AI looks at technician speed, historical performance, job difficulty, travel load, and shift duration, then distributes work so nobody is overloaded or underutilized.
Reducing Fuel Costs
Backtracking is one of the biggest hidden cost drains. AI reduces it by grouping nearby stops, avoiding cross-city zigzagging, and sequencing jobs in a smooth geographic flow.
Maximizing Jobs Per Day
By improving sequencing, reducing drive time, and predicting delays, AI creates additional space in the technician’s day, often enough to complete 1-2 more jobs without extending the shift.
This is the multi-objective balancing act that makes AI routing far more efficient than traditional methods.
Real-Time Adaptation: When the Day Changes
Even the best morning plan can’t survive a real workday without adjustments. Jobs run long, traffic slows down, and emergencies arrive.
This is where AI separates itself from manual planning. Instead of rebuilding the entire schedule, it makes small, targeted fixes in seconds.
What AI Monitors
AI routing systems continuously scan for:
- Technicians running behind
- Traffic spikes on upcoming routes
- Emergency job requests
- Customer cancellations
- Jobs at risk of missing time windows
How AI Recalculates
When something changes, AI doesn’t restart the whole plan. It performs focused re-optimization:
1. Isolates only the affected technicians and jobs
2. Protects high-priority customers and SLA deadlines
3. Finds the smallest possible adjustment
4. Reassigns or resequences only when necessary
5. Updates routes and customer ETAs instantly
This targeted approach keeps the rest of the schedule stable, the opposite of manual routing, where one delay can collapse several appointments.
Quick Example
Tech B is running 40 minutes behind after an unexpected issue.
AI Response (2-5 seconds):
- Detects the delay automatically
- Flags a 2 PM job as “at-risk”
- Evaluates nearby technicians’ availability
- Reassigns the job to Tech E (who’s ahead of schedule)
- Updates both routes and sends a new ETA to the customer
No dispatcher intervention. Customer gets an accurate arrival time. Tech B catches up without stress.
Manual vs. AI: Side-by-Side
| Capability | Manual Dispatcher | AI Route Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Jobs evaluated simultaneously | 10-15 | Unlimited |
| Route combinations considered | Dozens | Millions |
| Time to build daily schedule | 45-90 minutes | 1-5 seconds |
| Time to reshuffle after disruption | 15-30 minutes | 2-5 seconds |
| Typical efficiency achieved | 60-75% | 92-97% |
| Multi-objective optimization | One factor at a time | Simultaneous |
| Learning from history | Informal | Systematic |
The Results
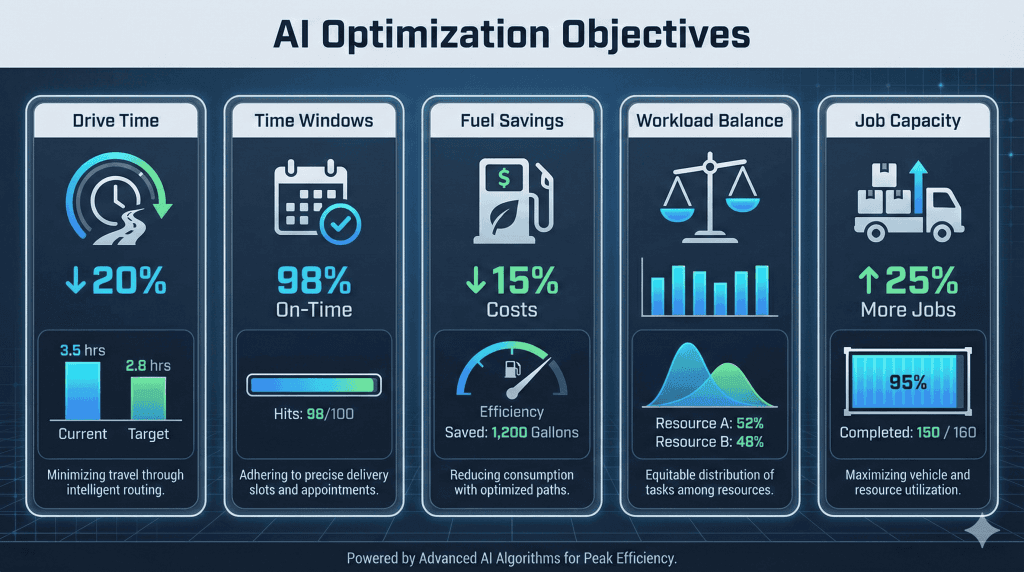
Based on real implementations, teams using AI route optimization typically see:
- 25-30% reduction in average drive time per technician
- 15-20% increase in jobs completed per day
- 96%+ on-time arrival rates
- 60-70% reduction in dispatcher workload for routine reshuffling
The operational impact compounds daily: fewer wasted miles, more completed jobs, consistent on-time arrivals, and dispatchers freed from constant schedule firefighting.
Who Benefits Most?
AI route optimization becomes essential once a team handles unpredictable schedules or high daily job volume:
Teams running HVAC service operations feel this first: when a 2-hour install turns into 4 hours, the whole day collapses without automated rerouting.
Plumbing companies deal with emergency leaks and same-day requests that demand instant schedule adjustments. Manual planning simply can’t keep up.
For electrical contractors, the challenge is different: certification requirements and skill-specific jobs mean the wrong tech on the wrong job creates callbacks and compliance issues.
Pest control businesses run dense, multi-stop routes where shaving 5 minutes per stop adds up to hours saved by the end of the day, especially during seasonal spikes.
Appliance repair teams face wildly variable job durations. A simple diagnostic can turn into a 3-hour repair, and AI adjusts downstream ETAs automatically.
Utility companies with large territories need multi-day planning across wide geographic areas, a problem that grows exponentially without algorithmic support.
Conclusion
AI route optimization solves the Vehicle Routing Problem, a mathematical challenge humans can’t compute at scale. Instead of spending 90 minutes building routes that break by noon, dispatchers using AI generate optimized schedules in seconds and adapt instantly to disruptions.
The difference isn’t just speed. It’s predictability. Routes that work in the real world, not just on paper.
Every Extra Mile Driven Is Money Lost
AI routing cuts hidden costs you don’t even realize you’re paying. Unlock your real daily capacity.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does AI handle emergency jobs?
AI evaluates all active routes in real time to find the optimal insertion point. It considers each technician’s current location, remaining jobs, skills, and time window constraints, then calculates who can reach the emergency fastest while causing the least disruption. This happens in 2-5 seconds.
What’s the Vehicle Routing Problem?
VRP is the mathematical challenge of determining optimal routes for multiple technicians visiting multiple locations while minimizing total distance, time, or cost. For context: 10 jobs create 3.6 million possible combinations. That’s why algorithms are necessary, not optional.
Can AI routing reduce fuel costs?
Yes. By eliminating backtracking, optimizing stop sequences, and clustering jobs geographically, AI typically reduces fuel costs. Plus, reduced drive time means technicians complete more billable jobs per day.
How is this different from Google Maps?
Google Maps finds the fastest route between two points. AI route optimization determines the optimal sequence of stops for multiple technicians across dozens of jobs, while respecting time windows, skills, workload balance, and business constraints. It’s the difference between “how do I get from A to B?” and “in what order should 8 technicians visit 50 customers?”
Does AI routing replace dispatchers?
No. AI removes the computational burden, evaluating millions of combinations, recalculating when disruptions occur, and balancing competing priorities. Dispatchers focus on judgment calls, customer relationships, and situations that need human insight.

