Your best technician just gave two weeks’ notice. Again.
And you know exactly why. They’ve been carrying the team for months while watching others coast with half the workload. They never complained until they found a job somewhere else.
This story plays out in field service companies every single day. The people who leave aren’t the ones coasting. They’re your best performers who finally got tired of being punished for being reliable.
What is technician burnout?
Technician burnout is the physical and emotional exhaustion that happens when field service technicians face chronic workload imbalance, unfair job distribution, or unsustainable scheduling patterns.
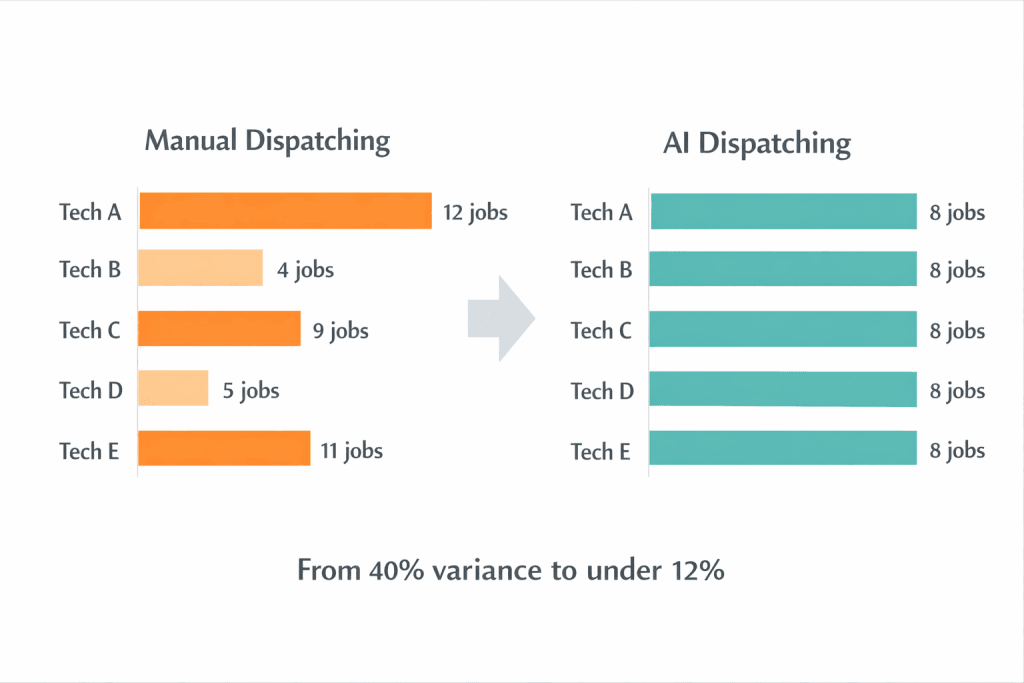
In AI dispatching, burnout typically shows up as visible inequality; one technician receives 10 jobs while another gets 4 on the same shift. This creates resentment, declining performance, and eventually resignation. The pattern is predictable: your most capable technicians absorb the hardest work until they can’t anymore.
The financial hit from burnout shows up gradually, in overtime expenses, declining service quality, and customer complaints. But by the time someone actually quits, you’ve already lost tens of thousands in replacement costs. Plus all the knowledge that just walked out the door.
This article breaks down the three types of workload imbalance that cause burnout, explains how AI dispatching mathematically enforces fairness. It helps us understand why catching burnout early costs a fraction of replacing the technicians you lose.
What Causes Technician Burnout in Field Service?
Manual dispatching creates predictable patterns of unfairness that destroy team morale over time. These patterns aren’t intentional. Dispatchers aren’t trying to overwork anyone. But when you’re making scheduling decisions under pressure, certain habits form, and those habits systematically burn out your best people.
Three types of workload imbalance drive technician burnout.
1. Volume Inequality
Volume inequality is the simplest form: one technician gets significantly more jobs than another on the same shift. Tech A has 10 stops. Tech B has 4.
How does this happen? Dispatchers under pressure default to their most reliable technicians. When a job absolutely needs to get done right, they send the person they trust most.
It’s not favoritism, it’s practical decision-making in the moment.
The problem is that “trusted” technician becomes the default for every difficult situation. Every tight deadline. Every demanding customer. Over weeks and months, this compounds.
Your reliable technician handles 40% more volume than their peers, not because they’re being rewarded, but because they’re being punished for being good at their job.
2. Complexity Clustering
All the difficult jobs funnel to senior technicians, while junior techs only handle routine work.
Picture an HVAC software company during summer peak season. The senior technician gets every “No Cool” emergency, complex diagnostics, frustrated customers, and high-pressure situations. Meanwhile, the junior technician handles maintenance calls, straightforward checklists, predictable timelines, and lower stakes.
Both work 8-hour shifts. One finishes exhausted and frustrated. The other finishes early with energy to spare.
The senior tech isn’t just doing more work. They’re doing harder work, with higher stakes, under more pressure. Complexity clustering accelerates burnout faster than volume alone because mental exhaustion compounds physical fatigue.
3. Geographic Unfairness
The technician covering the north zone drives 40% more miles than the one covering central, because nobody tracks cumulative distance across a full day.
When dispatchers assign jobs one at a time, they optimize for the immediate decision: “Who’s closest right now?” That makes sense in the moment.
But nobody accounts for cumulative impact.
By the end of the day, one technician has driven 120 miles while another has driven 70, despite handling the same number of jobs.
Geographic unfairness compounds with fuel costs, vehicle wear, and simple fatigue. The technician who drives more arrives at each job more tired, has less time for thorough work, and ends each day more drained than their peers.
For more on why manual dispatching fails at these calculations, see our comparison of AI dispatching vs traditional dispatch software.
Why Visible Inequality Destroys Morale Faster Than Anything Else
Workload imbalance destroys morale faster than almost any other workplace issue, because technicians can see the unfairness happening in real time.
Every technician starts their morning the same way. They open their mobile app and see their schedule: 10 stops, back-to-back, tight time windows, complex jobs. Then they talk to their colleague at the coffee machine. Four stops. Easy maintenance calls. Done by 3 PM.
This comparison happens every single day. In the old days of paper dispatch boards, technicians might not discover the imbalance until end-of-week conversations. Now, mobile apps make job counts immediately visible to the entire team.
When Tech A consistently sees more jobs than Tech B, three things happen.
Perception of Favoritism Develops Fast
Within two or three weeks of visible imbalance, technicians start concluding, whether accurate or not. “The dispatcher likes Tech B better.”
“Tech B must be complaining about the workload.”
“I’m being punished for being reliable.”
These perceptions erode trust in every dispatch decision, even the fair ones.
The “Always Available” Penalty Kicks In
In manual dispatching, the technician who never complains, always answers their phone, and consistently finishes jobs on time gets punished with the heaviest workload. Dispatchers naturally route difficult jobs to reliable people. It makes sense when you need something done right, you send your best.
But this creates a perverse incentive: the best way to reduce your workload is to become less reliable. Answer calls more slowly. Finish jobs later. Push back on difficult assignments. The technicians who figure this out protect themselves. The ones who don’t burn out.
Trust in Scheduling Collapses
Once trust is gone, every scheduling decision becomes suspect. Even legitimate business reasons for assignment patterns get interpreted through the lens of favoritism. “Why did I get this emergency? Because I’m closest, or because I’m the dumping ground?”
Your most valuable team members carry the heaviest loads while watching less reliable colleagues coast. And they remember every single instance.
To understand how AI evaluates fairness across multiple variables simultaneously, see our guide on how AI dispatching thinks.
Stop Invisible Workload Imbalance
FieldCamp tracks workload across your entire team, so you catch unfairness before it becomes a resignation letter.
How Does FieldCamp’s Workload Balancing Work?
FieldCamp prevents burnout through mathematical enforcement of fairness, not dispatcher promises or good intentions. The system uses constraint weights that make balanced distribution a core part of every scheduling decision.
The technicianWorkloadBalance Constraint
FieldCamp enforces fairness through something called the technicianWorkloadBalance constraint. Think of it as a dial that controls how aggressively the system prevents workload imbalance.
Here’s how it works:
- Default setting: 5000
- Configurable range: 1000 to 10,000
- Purpose: Mathematically prevent any single technician from being overloaded while others remain underutilized
This constraint weight tells the AI how much to prioritize fairness relative to other factors like drive time, time windows, and skill matching. A higher weight means stricter fairness enforcement. A lower weight gives more flexibility for route efficiency.
How the Weight Affects Real Decisions
When a new job arrives, FieldCamp’s AI evaluates every possible technician assignment. For each option, it calculates a score based on travel time to the job, skill match quality, time window fit, and current workload balance.
The technicianWorkloadBalance weight determines how heavily workload factors into this calculation. At the default setting of 5000, the system will accept meaningful trade-offs in other areas to maintain fair distribution.
Example: A P0 emergency arrives—highest priority, needs immediate response. Tech A already has 7 jobs assigned. Tech B has 4 jobs. Tech A is 8 minutes closer to the emergency.
With workload balancing enabled, the system assigns the emergency to Tech B, even though Tech A is closer. The additional drive time is an acceptable trade-off to prevent overloading someone who’s already busy.
For a deeper dive into the math behind fair distribution, see our guide on fair distribution algorithms.
Configuring for Your Business
Different businesses need different fairness levels. Here’s what typically works:
| Business Type | Recommended Weight | Why |
| Residential HVAC/Plumbing | 7500–10000 | Technicians see each other daily; fairness perception matters most |
| Commercial Maintenance | 3000–5000 | Efficiency often matters more than perfect balance |
| Mixed Residential/Commercial | 5000–7500 | Balance both concerns |
Daily Workload Balance for Multi-Day Fairness
FieldCamp also includes a dailyWorkloadBalance constraint (default: 1, range: 1–100) that works alongside technician-level balancing.
This prevents situations where one technician has a light Monday but crushing Tuesday through Friday, while another has the opposite pattern. The system considers workload distribution across your entire planning horizon, not just today’s schedule.
A technician who had a brutal Monday shouldn’t get another brutal Tuesday. The system remembers and compensates automatically.
Why Is Preventing Burnout 10× Cheaper Than Replacing Technicians?
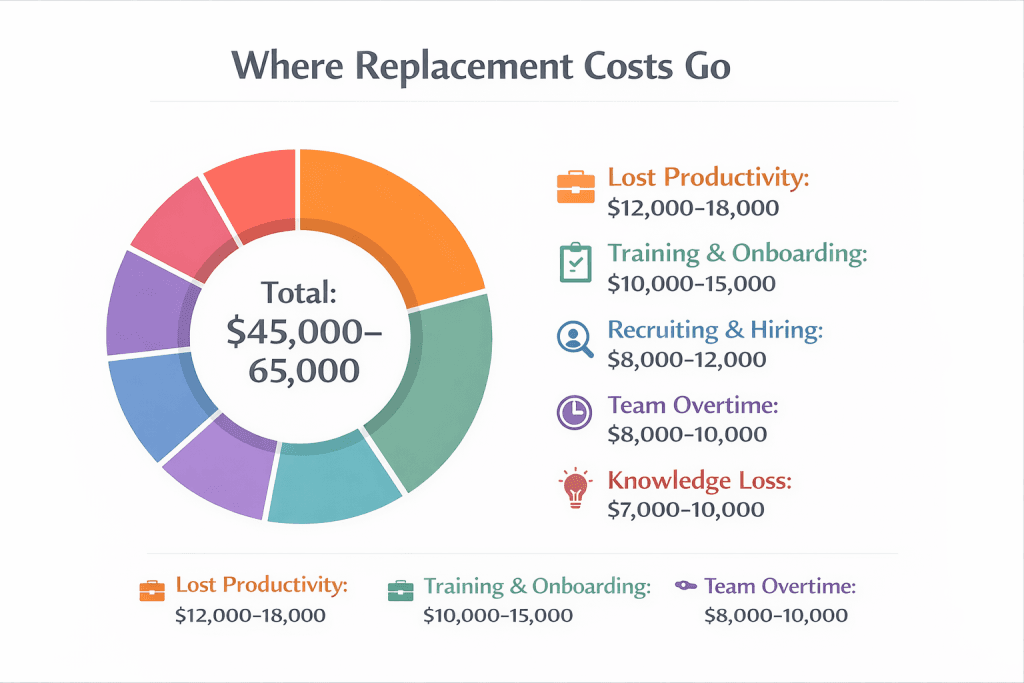
Replacing a burned-out technician costs far more than most contractors realize. When you factor in recruiting, training, lost productivity, and knowledge loss, the total typically runs between $45,000 and $65,000 per replacement.
That number includes job postings and recruiter fees, interview time for your team, four to eight weeks of reduced productivity during onboarding, coverage gaps while remaining team members pick up slack, and the customer relationships and equipment knowledge that walked out the door.
For specialized trades like HVAC or electrical, replacement costs often run even higher when you factor in certification requirements and the time needed to build customer trust.
Hidden Costs Beyond Direct Replacement
The replacement figure doesn’t capture everything that goes wrong when someone leaves.
1. Team morale takes a hit. When one technician leaves due to burnout, others notice. They start wondering if they’re next, especially if they’re carrying heavy workloads themselves.
2. Dispatcher stress increases. Covering gaps with fewer technicians means more complex scheduling decisions under more pressure. This often accelerates the same patterns that caused the first resignation.
3. Customer service suffers. New technicians don’t know customer preferences, equipment history, or site-specific details. Service quality drops during the transition period.
4. Overtime costs spike. Remaining technicians work overtime to cover gaps, which accelerates their own burnout risk. One resignation can trigger a cascade.
Industry-Specific Burnout Triggers
Different field service industries face different peak-season pressures that accelerate burnout:
HVAC: Summer peaks with “No Cool” emergencies and winter peaks with “No Heat” calls create sustained high-pressure periods where your best techs get hammered.
Plumbing: Winter pipe freezes create sudden demand spikes. The summer construction season creates sustained high volume. Both patterns stress your most capable people.
Electrical: Permit-dependent backlogs create unpredictable workload clustering. When permits clear, everything hits at once.
Real scenario: An HVAC company loses its senior technician in July, peak cooling season. Finding a replacement takes 8 weeks.
The cost exceeds $50,000 when you include recruiting, training, and overtime for the remaining team. Revenue impact during the busiest period extends far beyond direct replacement costs.
The Prevention Math
AI dispatching software costs a fraction of a technician replacement. When you prevent even one resignation through fair workload distribution, you’ve typically saved many times the annual cost of the software.
For help calculating this for your specific operation, see our AI dispatcher ROI calculator.
How to Balance Workload Fairness vs Route Efficiency
Fair workload distribution sometimes conflicts with pure route efficiency. Understanding this trade-off helps you configure the system for what actually matters to your business.
The Fairness vs Efficiency Slider
Think of FieldCamp’s technicianWorkloadBalance weight as a slider between two priorities:
Higher weight (7500–10000): Prioritize fairness, accept some efficiency loss. The system will send jobs to less-loaded technicians even if they’re not the closest option.
Lower weight (3000–5000): Prioritize efficiency, accept some workload imbalance. The system optimizes routes more aggressively, which may concentrate jobs on certain technicians.
Neither extreme is right for every situation. The optimal setting depends on your operational context.
When to Prioritize Fairness?
Customer-facing residential businesses should typically set workload balance higher (7500–10000):
- Technicians interact regularly and compare workloads
- Team morale directly affects customer experience
- Turnover costs are high relative to marginal efficiency gains
- Repeat customers expect consistent service quality
In these environments, the efficiency cost of fair distribution is small compared to the morale and retention benefits. Effective team management depends on visible fairness.
When to Prioritize Efficiency?
Efficiency-focused operations can lower the weight (3000–5000):
- Commercial maintenance routes where technicians work independently
- Warranty work with tight margin constraints
- High-volume, low-complexity job types
- Situations where some technicians genuinely prefer heavier workloads
In these environments, technicians may be less aware of peer workloads, and the business may need every minute of efficiency to maintain profitability.
For more on how route optimization interacts with workload balancing, see our guide on AI route optimization explained.
Multi-Day Workload Accumulation
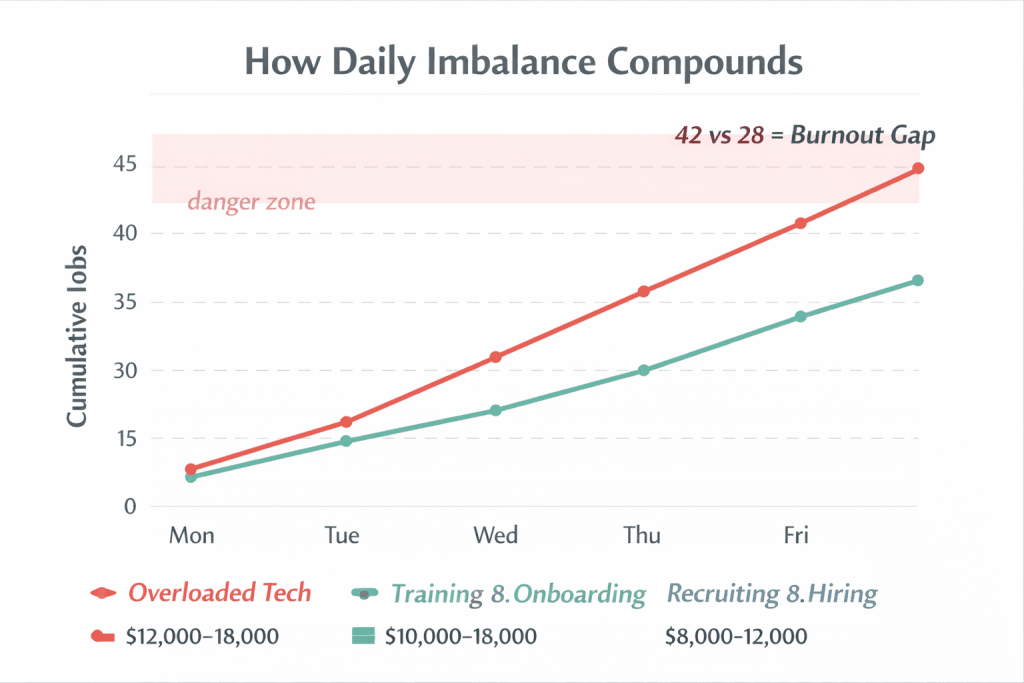
Poor Monday distribution compounds into Friday burnout.
Tech A receives 42 jobs across the week. Tech B receives 28. By Friday, Tech A is exhausted, making mistakes, and mentally composing their resignation letter. They’re not burned out from one bad day; they’re burned out from a pattern that nobody caught.
FieldCamp’s dailyWorkloadBalance constraint addresses this by considering cumulative workload across your planning horizon. The system doesn’t just balance today. It balances the week.
How Does FieldCamp Prevent Burnout Before It Happens?
FieldCamp prevents burnout through three mechanisms: real-time workload monitoring, emergency insertion protection, and transparent job distribution.
Real-Time Workload Monitoring
FieldCamp continuously tracks workload distribution across your team. When imbalances emerge, before they become burnout patterns, the system flags them for attention.
This monitoring happens automatically, without requiring dispatchers to run reports or manually compare schedules.
The AI watches for single-day workload spikes, multi-day accumulation patterns, skill-based bottlenecks where specialists get overloaded, and geographic clustering that puts excessive miles on certain technicians.
Protection During Emergency Insertion
When a P0 emergency arrives, traditional dispatch systems typically assign it to whoever is closest, regardless of their current workload. This punishes reliable technicians who happen to be in the right location.
FieldCamp protects already-loaded technicians during dynamic rerouting. The system evaluates current job count for each candidate, remaining capacity within shift constraints, downstream impact on other scheduled jobs, and skill match combined with geographic proximity.
Learn more in our job management documentation.
Only after considering all factors does the system make an assignment. A technician with 7 jobs won’t automatically receive an emergency when another qualified technician has 4, even if the busier technician is slightly closer.
Workload Transparency for Technicians
One of the most powerful burnout prevention tools is simple transparency. When technicians can see that job distribution is fair, that the system is actively balancing workload, they trust the process.
With AI job scheduling, technicians see their daily assignments alongside context about why they received them. This visibility builds trust in ways that manual “black box” dispatching never can.
When a technician sees they have 8 jobs and their colleague has 7, they understand the distribution is balanced. When they had a heavy Monday, they saw Tuesday lighten up. The fairness isn’t invisible anymore, it’s demonstrable.
What Makes This Different
The difference between FieldCamp and basic scheduling tools isn’t just automation; it’s mathematical accountability. Workload balance isn’t a goal someone hopes to achieve. It’s a constraint the system enforces on every single scheduling decision.
Your best technicians aren’t punished for being reliable. Workload distribution is mathematically fair. Burnout patterns get caught before they cause resignations through real-time team management visibility.
Wrapping Up
When your best technician finally quits because they’ve been carrying the team, the replacement cost is just the beginning. You lose their customer relationships, their equipment knowledge, their reliability, everything that made them valuable in the first place.
Fair workload distribution with AI dispatching prevents this scenario by mathematically enforcing balance. Not through dispatcher promises. Not through good intentions. Through algorithmic constraints that protect your most reliable technicians from becoming your most burned-out ones.
Preventing one resignation saves many times the annual cost of AI dispatching software.
Beyond the direct savings, fair workload distribution improves team morale, customer service quality, and operational stability. Your best people stay because they can see they’re being treated fairly.
Keep Your Best Technicians
Watch FieldCamp distribute jobs fairly across your team in real time, without sacrificing route efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does AI dispatching prevent technician burnout?
AI dispatching prevents burnout by mathematically enforcing fair workload distribution through constraint weights. FieldCamp’s technicianWorkloadBalance setting ensures no single technician gets overloaded while others remain underutilized. The system tracks workload across days and weeks, automatically compensating when someone has a heavy day by lightening their subsequent schedule. This eliminates the visible inequality that destroys team morale and drives resignations.
What is the 10-job vs 4-job problem?
The 10-job vs 4-job problem describes what happens when manual dispatching assigns 10 jobs to one technician and only 4 to another on the same shift. This visible inequality is immediately apparent through mobile apps; every technician can see their schedule and compare it to colleagues. The unfairness compounds daily, creating resentment that builds until someone quits. AI dispatching solves this by balancing job counts as a core constraint, not an afterthought.
How much does it cost to replace a burned-out technician?
Replacement costs typically $55,000 average when you account for recruiting, training, lost productivity during onboarding, and institutional knowledge loss. For specialized trades requiring certifications, costs often exceed $60,000. This doesn’t include indirect costs like decreased team morale, increased overtime for remaining staff, and customer service disruptions during the transition period.
Can I prioritize route efficiency over workload fairness?
Yes. FieldCamp’s technicianWorkloadBalance weight is fully adjustable from 1000 to 10,000. Efficiency-focused operations can lower the weight to 3000–5000, which optimizes routes more aggressively while accepting some workload imbalance. Customer-facing residential businesses typically set it higher (7500–10000) because team morale and retention matter more than marginal efficiency gains. The right setting depends on your specific operation and team dynamics.