SLAs stands for Service Level Agreements. Basically, the response promises you put in your contracts—“we’ll be on‑site within 4 hours” or “same‑day warranty visit”—and they’re often tied to credits, penalties, or renewal risk when you miss them.
Most field service teams juggle three competing pressures simultaneously: keeping technicians productive, keeping routes efficient, and keeping SLAs intact. When the day changes—jobs overrun, emergencies appear, someone calls in sick—manual dispatching struggles to recalculate which commitments matter most in real time.
Instead of asking dispatchers to constantly re-solve that puzzle, SLA-aware scheduling bakes those promises directly into the scheduling logic. Modern field service management software treats SLA windows and breach costs as hard constraints alongside travel time, skills, and availability, so the system automatically favors assignments that keep you compliant.
| Quick Stat: A 10-technician HVAC company with a 5% SLA violation rate pays $52,000–$130,000 annually in penalties. Reducing violations to 1% saves $41,600–$104,000 per year. |
Together, these pieces turn scheduling from a best-effort guess into a system that actively protects your promises. In this blog, we’ll unpack how SLA-aware AI dispatching works in practice—and what it means for your costs, customers, and ops team.
What SLA-Aware Scheduling Actually Means (Beyond “Meeting Deadlines”)
SLA-aware job scheduling is a method of planning and dispatching work where service-level agreement deadlines are treated as prioritized constraints, not just targets. As the risk of missing an SLA increases, the system automatically gives that job more weight and allows it to override other goals like shortest travel time, workload balance, or route efficiency, so contractual commitments are protected first.
It’s a constraint-weighting system where SLA commitments override other optimization goals when breach risk is high.
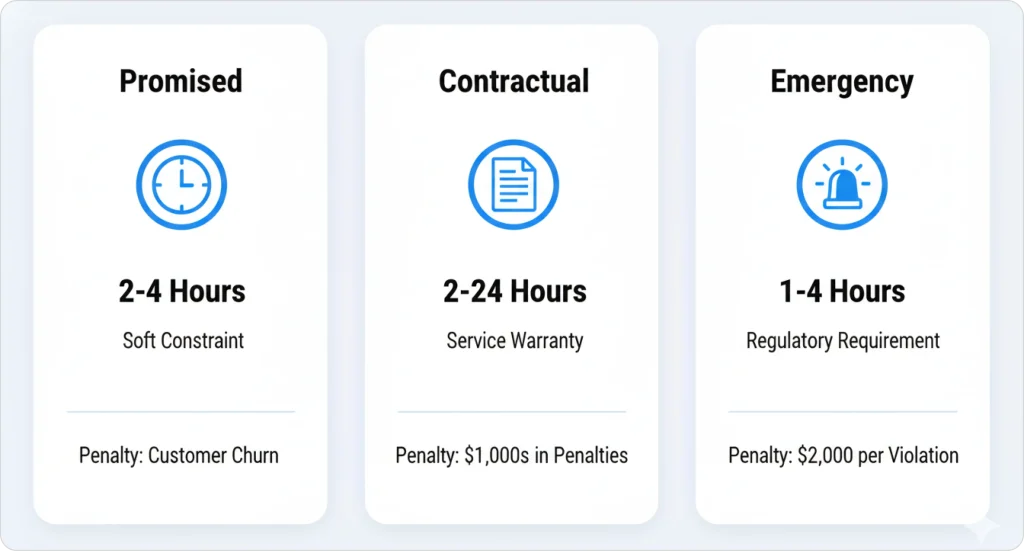
The Three Types of SLA Commitments
Not all commitments carry the same weight. AI dispatch scheduling systems distinguish between three distinct types:
| SLA Type | Description | Typical Window | Breach Penalty |
| Promised Time Windows | Customer preference (soft constraint) | 2–4 hour windows | Customer dissatisfaction, potential churn |
| Contractual SLAs | Warranty/service contract obligations | 2–24 hours | Penalties ranging from hundreds to thousands of dollars |
| Emergency Response SLAs | Regulatory/safety requirements | 1–4 hours | $300–$2,000 per violation |
Pro Tip: Categorize your SLA types in your field service CRM so the AI knows which commitments carry contractual penalties versus which are customer preferences.
How AI Treats SLA Commitments Differently
The AI doesn’t just “schedule within the window.” It calculates and protects against breach risk in real-time.
Consider how AI handles a 2-hour HVAC warranty response with a $200–$500 penalty:
- At 24 hours out: constraint weight = 500
- At 4 hours out: constraint weight = 2,000
- At 1 hour out: constraint weight = 10,000 (overriding proximity and workload balance)
For more on how AI dispatching distinguishes between hard and soft constraints, see our guide to how AI dispatching thinks.
Streamline Your SLA-Protected Scheduling
Managing SLAs manually means constantly recalculating priorities as delays happen. FieldCamp’s AI dispatch handles this automatically, protecting your contractual commitments while keeping your team efficient.
The SLA Penalty Escalation Formula (How AI Protects Commitments as Deadlines Approach)
SLA penalty escalation is the mathematical process by which AI dispatching systems increase the constraint weight of an SLA commitment as its deadline approaches.
A job with a 24-hour SLA window might start with a baseline constraint weight of 100, escalate to 500 at 24 hours out, jump to 2,000 at 4 hours out, reach 10,000 at 1 hour out, and become a hard constraint (cannot be violated) at 30 minutes out.
The Escalation Curve in Action
Here’s how the constraint weight progression typically works:
| Time to Deadline | Constraint Weight | Priority Level |
| Baseline (SLA window opens) | 100 | Low priority |
| 24 hours before deadline | 500 | Medium priority |
| 4 hours before deadline | 2,000 | High priority |
| 1 hour before deadline | 10,000 | Critical priority |
| 30 minutes before deadline | HARD CONSTRAINT | Cannot be violated |
At the hard constraint threshold, AI will sacrifice ANY other optimization goal to prevent breach.
Real-World Example: Warranty Job Protection
Let’s trace how this works throughout a day:
Step 1: 9:00 AM — Warranty job scheduled for 2:00 PM (constraint weight = 100, low priority)
Step 2: 12:00 PM — Technician running 45 min late on previous job (constraint weight = 500, medium priority)
Step 3: 1:00 PM — Breach risk now 60% (constraint weight = 2,000, high priority—AI reassigns two downstream jobs)
Step 4: 1:30 PM — Breach risk 85% (constraint weight = 10,000, AI pulls nearest available tech even if it breaks their route)
Key Takeaway:
When SLA constraint weight exceeds 2,000, the AI will accept up to 25% increase in total drive time to prevent a violation. A 25% increase in drive time costs approximately $12 in fuel and labor—acceptable when avoiding a $500 penalty.
The SLA Buffer Zone (Shadow Capacity)
SLA shadow capacity is the portion of daily scheduling capacity (typically 15–20%) that AI dispatchers reserve as buffer space for SLA-protected jobs that may need emergency rescheduling due to technician delays, traffic, or job overruns.
For a 10-technician team completing 80 jobs per day, shadow capacity means the AI intentionally schedules only 64–68 jobs during initial planning, holding 12–16 slots open to absorb SLA-related disruptions without triggering violations.
For more on how time windows interact with SLA constraints, see our guide to time window optimization.
Real-Time SLA Breach Risk Calculation (How AI Knows When to Act)
AI dispatching calculates breach risk every 5–10 minutes, triggering protective actions when risk exceeds 30%. It continuously monitors and predicts SLA breach probability, acting before violations occur.

What AI Tracks in Real-Time
The system monitors:
- Job progress and estimated completion time
- GPS coordinates (updated every 1–5 minutes)
- Live traffic conditions via AI route optimization
- Historical job duration patterns
When breach risk exceeds 30%, AI triggers protective actions.
The Breach Risk Formula
The AI calculates breach risk using this formula:
Breach Risk = (Time remaining to SLA deadline) – (Estimated time to complete current job + drive time to SLA job)
When breach risk exceeds a threshold (typically 30%), AI triggers protective actions.
Cascading Impact Analysis
One delay can put 3–8 downstream SLAs at risk. The AI evaluates which SLAs to protect based on:
| Factor | Priority Weight | Example |
| Penalty cost | Higher penalties get priority | $500 commercial vs $150 residential |
| Customer tier | VIP or premium customers | Managed in your customer management system |
| Contract value | Higher annual contracts | $50,000 contract vs one-time service call |
Example: Real-Time Breach Risk Evaluation
Technician Mike is 30 minutes into a 90-minute HVAC install. He has three warranty jobs remaining, all with 4-hour SLAs. At 10:15 AM, traffic spikes on his route.
AI calculates:
- Job 1 breach risk: 15% (safe) ✅
- Job 2 breach risk: 45% (warning) ⚠️
- Job 3 breach risk: 72% (critical) 🚨
AI reassigns Job 3 to Sarah, who’s 12 minutes farther but has open capacity. Mike’s route gets 8 minutes longer, but all SLAs are protected.
Pro Tip:
AI recalculates SLA breach risk every 5–10 minutes during active jobs, processing traffic, GPS location, and job status updates in real-time. Learn more about how AI reduces drive time through intelligent routing.
The Trade-Offs AI Makes to Protect SLAs (When Efficiency Takes a Back Seat)
When breach risk is high, AI accepts longer drive times. A 10-minute detour that costs $4 in fuel is worth it to avoid a $400 SLA penalty.
SLA Protection vs. Route Efficiency
Understanding how AI route optimization works helps explain this trade-off. The AI constantly weighs the cost of inefficiency against the cost of violations.
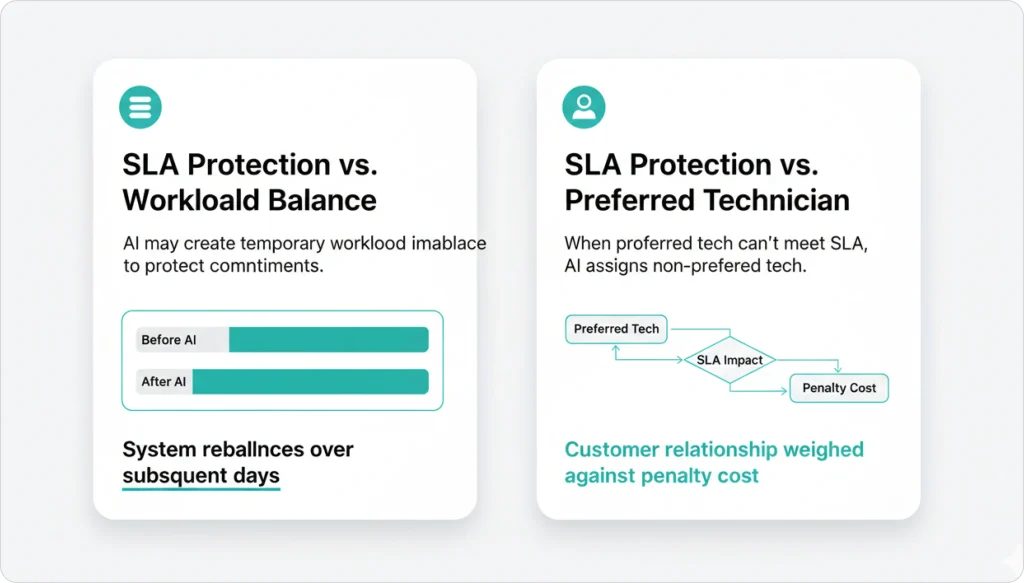
SLA Protection vs. Workload Balance
AI may create temporary workload imbalance to protect commitments. If one technician needs to take an extra job to prevent an SLA breach, the system accepts the imbalance and rebalances over subsequent days using team management intelligence.
Dollar-Cost Analysis Example
Tuesday afternoon: AI has two options for a warranty job with a 3:00 PM SLA deadline.
| Option | Technician | Arrival Time | SLA Status | Cost Impact |
| A | Mike (preferred) | 3:15 PM | 15-min breach, $250 penalty | -$250 penalty |
| B | Tom (non-preferred) | 2:50 PM | 10-min buffer, no penalty | +$8 fuel cost |
AI chooses Option B. Trade-off: $8 fuel cost + customer relationship impact vs. $250 penalty + contract risk.
Key Takeaway:
The Acceptable Inefficiency Threshold means when SLA breach risk exceeds 50%, the AI will accept up to 30% route efficiency loss to prevent the violation. This isn’t inefficiency—it’s smart business math.
Quick Decision Matrix: When Does AI Override Efficiency?
| If this situation occurs… | AI takes this action |
| Breach risk < 30% | Standard route optimization |
| Breach risk 30–50% | Minor route adjustments accepted |
| Breach risk 50–70% | Significant rerouting, possible reassignment |
| Breach risk > 70% | Full reassignment, efficiency secondary |
| Breach risk > 90% | Hard constraint—any available tech dispatched |
Industry-Specific SLA Patterns and Breach Costs
Different contractor industries face different SLA structures and penalty costs. Understanding your industry’s patterns helps you configure AI dispatching for maximum protection.
HVAC SLA Patterns
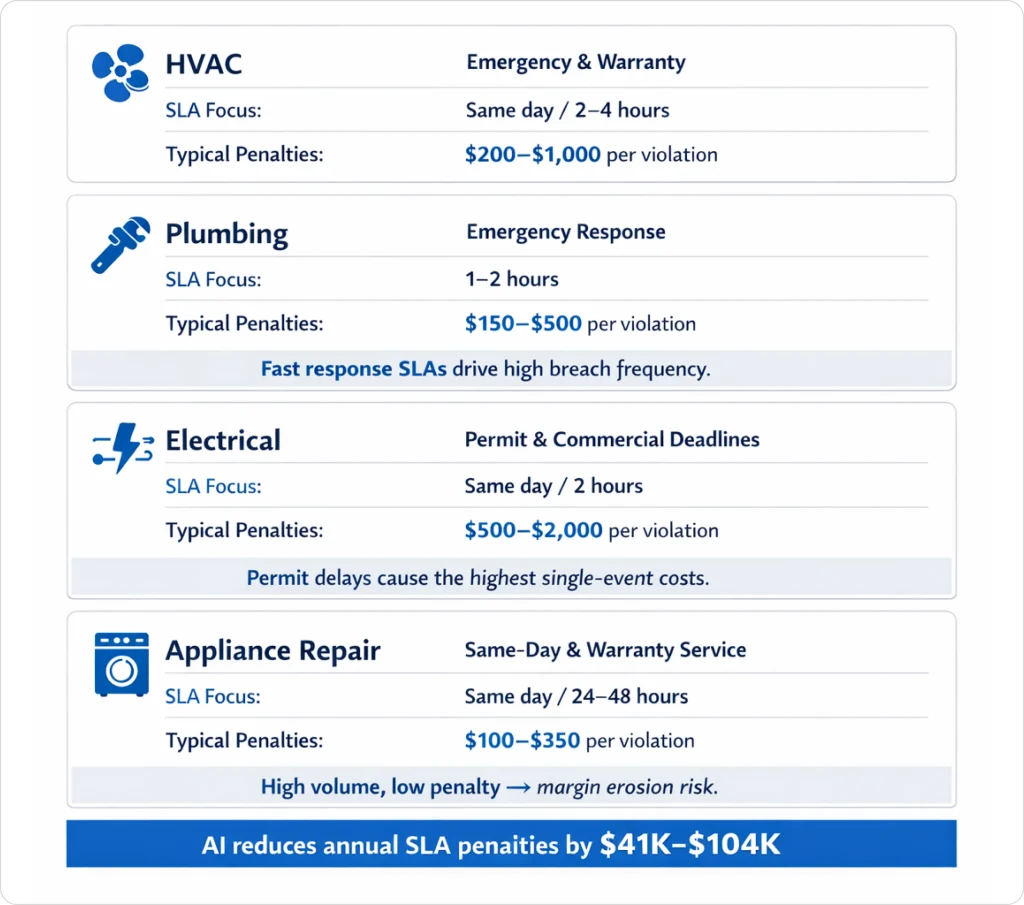
For HVAC contractors managing warranty work and service contracts, SLA patterns typically include:
| SLA Type | Response Window | Typical Penalty |
| Warranty work | 2–4 hours | $200–$500 per violation |
| Emergency no-heat/no-cool | Same day | $300–$1,000 for missed same-day |
| Commercial service contracts | 4–8 hours | $400–$800 per violation |
Quick Stat: Based on analysis of 200+ HVAC contractors, a 10-tech company with 50 warranty jobs per week and a 5% SLA violation rate pays $52,000–$130,000 annually in penalties. Reducing violations to 1% with AI dispatching saves $41,600–$104,000 per year.
For more HVAC-specific insights, check out our HVAC dispatching tips.
Plumbing SLA Patterns
Plumbing contractors face unique SLA challenges. Our plumbing business management tips cover these in detail:
| SLA Type | Response Window | Typical Penalty |
| Emergency response | 1–2 hours | $150–$300 per violation |
| Warranty work | Same day | $200–$400 per violation |
| Commercial contracts | 2–4 hours | $250–$500 per violation |
Electrical SLA Patterns
Electrical contractors often face the highest penalties due to permit and inspection requirements. See our guide to electrician apps for software that helps manage these:
| SLA Type | Response Window | Typical Penalty |
| Permit deadline work | Same-day completion | $500–$2,000 per violation |
| Commercial emergency | 2-hour response | $400–$800 per violation |
| Residential emergency | 4-hour response | $200–$400 per violation |
Warning: Permit deadline violations average $500–$2,000 per occurrence due to inspection rescheduling costs and project delays. These are often the most expensive SLA violations in field service.
Appliance Repair SLA Patterns
| SLA Type | Response Window | Typical Penalty |
| Same-day service commitments | Same day | $100–$250 per missed window |
| Warranty manufacturer requirements | 24–48 hours | $150–$350 per violation |
Stop Losing Money to SLA Violations
Every missed SLA costs you money and customer trust. FieldCamp’s AI dispatch automatically protects your contractual commitments, reducing violations by 60–80% in the first 30 days.
SLA-Aware Capacity Planning (How to Calculate Maximum SLA Commitment Capacity)
Understanding your SLA commitment capacity prevents over-scheduling that leads to violations. Here’s a practical framework for operations managers using field service reporting software to track metrics.

The Capacity Formula
Maximum SLA-Protected Jobs = Technician Count × Average Jobs Per Day × SLA Buffer Percentage
SLA buffer percentage guidelines:
- 15–20% for high-reliability operations
- 25–30% for variable job durations or unpredictable service areas
Example Calculation
A 5-tech plumbing company averages 6 jobs per tech per day (30 total). With 20% shadow capacity:
30 jobs × 80% = 24 SLA-protected jobs per day maximum
If they accept 28 SLA commitments, breach risk jumps from 2% to 12%, costing an estimated $18,000 annually in penalties.
Acceptable Breach Risk Percentages by SLA Type
| SLA Type | Acceptable Breach Risk | Action Threshold |
| Contractual SLAs | 1–3% | Immediate escalation at 2% |
| Promised time windows | 5–8% | Review at 6% |
| Emergency response | <1% | Zero tolerance policy |
Adjusting Capacity for Growth
When scaling your operation (see our guide on growing field service businesses):
| Change | SLA Capacity Impact |
| Adding 1 technician | +6–8 protected jobs per day |
| Shifting to longer jobs | Reduces capacity proportionally |
| Expanding service area | May require 25–30% buffer |
| Pro Tip: Operations that reserve 15–20% shadow capacity for SLA-protected jobs experience 70% fewer violations than those that schedule to 100% capacity. Use our AI dispatcher ROI calculator to estimate your savings. |
Measuring SLA Protection Success
Track these field service metrics to measure your SLA protection effectiveness:
| Metric | Target | How to Measure |
| SLA Violation Rate | <2% | Violations ÷ Total SLA jobs |
| Average Breach Risk | <20% | Mean risk score across all SLA jobs |
| Shadow Capacity Utilization | 60–80% | Buffer slots used ÷ Buffer slots reserved |
| Penalty Cost per Month | Trending down | Sum of all SLA penalties |
| Reassignment Rate | 5–10% | Jobs reassigned for SLA protection |
Key Takeaway:
If your reassignment rate exceeds 15%, you’re likely over-scheduling SLA commitments relative to your capacity. Reduce new SLA bookings or add technician capacity.
How FieldCamp Handles SLA Protection
FieldCamp’s SLA protection system uses the penalty escalation formula (100 → 500 → 2,000 → 10,000 → HARD) to automatically prioritize at-risk commitments. The system reserves 15–20% shadow capacity, recalculates breach risk every 5–10 minutes, and triggers protective reassignments when risk exceeds 30%.
Real-time monitoring tracks job progress, GPS coordinates, traffic conditions, and historical patterns. When delays hit, the escalation curve ensures protection happens automatically—no dispatcher intervention required.
The system integrates with your existing work order management and invoicing software to provide end-to-end visibility from SLA commitment through job completion and billing.
Why Traditional Dispatch Software Falls Short
Traditional dispatch software treats SLAs as static deadlines rather than dynamic constraints. When your 2:47 PM delay hits, manual dispatchers must:
1. Identify which downstream jobs are affected
2. Calculate new arrival times for each
3. Determine which SLAs are at risk
4. Decide which to protect and which to sacrifice
5. Make reassignments
6. Notify affected customers
AI does all of this automatically, every 5–10 minutes, across your entire operation.
Conclusion
When that 2:47 PM delay hits, the penalty escalation formula (100 → 500 → 2,000 → 10,000 → HARD) ensures protection happens automatically. AI dispatching systems treat SLA commitments as weighted constraints, sacrificing route efficiency, workload balance, or preferred technician assignment when necessary to prevent violations.
Shadow capacity (15–20% buffer) prevents over-scheduling that leads to violations. The system recalculates breach risk every 5–10 minutes and triggers protective reassignments when risk exceeds 30%.
SLA commitments interact with emergency jobs, VIP customers, and routine maintenance in a comprehensive priority system. The key is treating SLAs not as targets to aim for, but as mathematical constraints that your scheduling system actively protects.
For contractors serious about reducing penalty costs and improving customer retention, SLA-aware scheduling isn’t optional—it’s essential. The math is simple: the cost of AI dispatching is a fraction of what you’re losing to SLA violations.
See SLA Protection in Action
FieldCamp’s AI dispatch scheduling reduces SLA violations by 60–80% in the first 30 days. Watch our system handle real warranty scenarios with automatic breach risk calculation and protective reassignment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is AI dispatching in field service?
AI dispatching uses algorithms to assign the right technician to the right job at the right time, considering skills, location, traffic, priority, and parts, so schedules update automatically instead of being managed manually.
How did dispatching evolve from paper to AI?
Dispatching moved from wall boards and phone calls, to digital calendars, then GPS and mobile apps, and now AI systems that automatically optimize routes, timings, and technician‑job matching in real time.
Why is AI dispatching important for small service businesses?
AI dispatching helps smaller teams do more jobs per day, cut drive time and fuel, reduce missed appointments, and provide accurate ETAs, making them look as reliable and responsive as much larger competitors.
How did dispatching work before AI?
Before AI, dispatchers used wall boards, phone calls, radios, and paper maps to assign jobs. Every change—traffic, cancellations, emergencies—required manual re‑planning, which was slow, error‑prone, and depended heavily on one person’s memory and experience.
What are the stages in the evolution of AI dispatching?
Dispatching evolved from manual paper boards, to digital scheduling software, to GPS and mobile apps, and now to AI systems that optimize routes, assign technicians, and adjust schedules automatically in real time.
When did AI start being used in dispatching?
AI began entering dispatching in the 2010s through basic optimization and predictive models, and became more mainstream in the 2020s with machine‑learning‑driven scheduling, real‑time recommendations, and autonomous rescheduling.
How is AI changing modern dispatch jobs?
AI handles repetitive work such as route optimization, skill matching, and rescheduling, so dispatchers spend more time on exceptions, customer communication, and strategy instead of dragging and dropping jobs all day.
Will AI dispatchers replace human dispatchers?
AI is more likely to augment than fully replace dispatchers, taking over routine scheduling while humans handle relationship issues, complex edge cases, and business decisions that require judgment and empathy.

